Introduction
The COVID-19 pandemic has affected tens of millions of individuals worldwide and has prompted important well being, social, and financial penalties. Iran, like many different nations, has skilled a excessive variety of instances and deaths because of the virus. In addition to the bodily well being influence, the pandemic has additionally prompted psychological misery, together with demise nervousness (Khademian et al., 2021; Zarei et al., 2021a,b; Jazaiery et al., 2022).
Health literacy (HL) is outlined because the diploma to which people have the capability to acquire, course of, and perceive primary well being data and companies wanted to make acceptable well being selections. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), well being literacy is a vital determinant of well being outcomes and has a big influence on people’ skill to entry and use well being companies successfully (Health literacy in Healthy People 2030, 2021).
Studies have proven that enhancing HL can have a optimistic influence on resilience, well being habits, and well-being (Barsell et al., 2018). In the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, well being literacy has turn into more and more vital as people search correct and well timed details about the virus and its influence on their well being. A research by Paakkari and Okan (2020) discovered that people with larger well being literacy have been extra prone to have interaction in preventive behaviors and had a greater understanding of the dangers related to COVID-19 (Paakkari and Okan, 2020). Low well being literacy is related to points comparable to inadequate understanding of well being data concerning worry of rising illnesses like COVID-19, much less participation in preventive behaviors, delayed prognosis of illnesses (Schulz and Rapaport, 2005), incapability to carry out self-care abilities (Von Wagner et al., 2007), and non-adherence to wholesome way of life behaviors (Wolf et al., 2005).
Generalized nervousness dysfunction (GAD) is a psychological well being situation characterised by extreme and chronic fear and nervousness about on a regular basis life occasions and actions. People with GAD might expertise signs comparable to restlessness, fatigue, issue concentrating, irritability, muscle rigidity, and sleep disturbance. The actual causes of GAD usually are not absolutely understood, however it’s believed to be a mix of genetic, organic, and environmental elements (Paulus et al., 2015). Generalized nervousness dysfunction is extra prevalent amongst people with restricted well being literacy (Rowlands et al., 2013).
The COVID-19 pandemic has had a big influence on psychological well being globally, together with a rise in nervousness and stress ranges. Several research have advised a possible affiliation between COVID-19 and GAD. A research from China discovered that people who had been in quarantine throughout the COVID-19 outbreak had larger ranges of tension and melancholy signs, together with GAD signs, in comparison with those that had not been quarantined (Wang et al., 2020).
An Italian research throughout the COVID-19 pandemic discovered that people with pre-existing psychological well being circumstances, together with GAD, have been at larger danger of experiencing extreme psychological misery throughout the pandemic (Mazza et al., 2020).
The affiliation between COVID-19 and GAD could also be associated to a number of elements, together with worry of an infection, uncertainty concerning the future, social isolation, monetary stress, and different pandemic-related stressors. Additionally, the pandemic has disrupted traditional routines and social help programs, which might exacerbate signs of GAD (Salari et al., 2020).
The relationship between well being literacy and GAD throughout the COVID-19 pandemic is a vital space of research. Health literacy refers to a person’s skill to entry, perceive, and use well being data to make knowledgeable selections about their well being (Paakkari and Okan, 2020). GAD, however, is a psychological well being situation characterised by extreme and chronic fear and nervousness (Paulus et al., 2015).
During the COVID-19 pandemic, people with larger well being literacy might have higher entry to correct and dependable well being data, resulting in a greater understanding of the virus, preventive measures, and out there healthcare assets. This elevated understanding might assist alleviate nervousness associated to the pandemic (Vahedian-Azimi et al., 2020).
Conversely, people with decrease well being literacy might face challenges in accessing and understanding well being data, which might contribute to heightened nervousness and uncertainty throughout the pandemic (Mohammadkhah et al., 2021).
However, it is very important word that the connection between well being literacy and GAD throughout COVID-19 is complicated and influenced by varied elements comparable to socioeconomic standing, training degree, cultural beliefs, and entry to healthcare companies. And there was restricted consideration given to its relationship with generalized nervousness dysfunction, globally in addition to in Iran. Several research carried out in Iran have investigated the psychological hyperlink between generalized nervousness dysfunction and COVID-19 (Vahedian-Azimi et al., 2020), whereas only some have explored the connection between COVID-19 nervousness and well being literacy (Mohammadkhah et al., 2021). Additionally, no such research has been carried out within the Khuzestan area which, with totally different races, cultures, and epidemiological elements, might have various ranges of well being literacy that may influence one’s understanding and response to well being data throughout the pandemic. Therefore, we designed this research to analyze the connection between well being literacy and generalized nervousness dysfunction ranges amongst residents of Khuzestan province throughout the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
Study design and gather the information
Tools of research
We used two customary questionnaires as follows:
1. “Iranian Health Literacy Questionnaire.” The questionnaire consists of 33 gadgets primarily based on a five-point Likert scale (1: Always, 2: Mostly, 3: Sometimes, 4: Rarely, 5: Never). The questionnaire has 5 elements, together with entry (gadgets 1–6), studying abilities (gadgets 7–10), understanding (gadgets 11–17), analysis (gadgets 18–20), and decision-making and utility of data (gadgets 21–33). The well being literacy rating ranges from 0 to 100 and is split into 4 ranges: insufficient (0–50), marginal (50.1–66), satisfactory (66.1–84), and glorious (84.1–100). In the current research, the satisfactory and glorious ranges are thought-about because the satisfactory degree (66.1–100). The Cronbach’s alpha coefficient for this questionnaire was reported to be 0.75 (Haghdoost et al., 2015).
2. The Generalized Anxiety Disorder-7 questionnaire consists of seven gadgets primarily based on a four-point Likert scale (1: Never, 2: Several days, 3: Nearly each day, 4: About half the times). The scores vary from 7 to 21, and better scores point out larger nervousness ranges. The Cronbach’s alpha coefficient for this customary questionnaire was reported to be 0.85 (Nayiniyan et al., 2011).
Ethical issues
This research was carried out with the help of the Social Determinant of Health Research Center (Reference No. SDH-9904), Deputy of Research in Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences with ethics committee quantity: IR.AJUMS.REC.1399.089.
Statistical evaluation
In this research, all statistical analyses have been carried out by utilizing STATA model 14 software program.
And for analytical: we used independed t-test, a method ANOWA. The degree of significance was lower than 0.05.
Results
The outcomes of this research have been obtained from 1,130 individuals within the age teams below research. There have been 40 people (3.5%) within the first age group, 522 people (46.2%) within the second age group, 525 people (46.5%) within the third age group, and 43 people (3.8%) within the fourth age group. In addition, there have been 552 males (48.8%) and 578 ladies (51.2%). There have been 875 married individuals (77.4%). The majority of individuals, 436 (38.6%), had a bachelor’s diploma, and 255 had an affiliate diploma, with the bottom proportion (22.7%). Regarding occupation, employed people had the best frequency with 638 (56.4%), and unemployed people had the bottom frequency with 55 (4.9%) (Table 1).
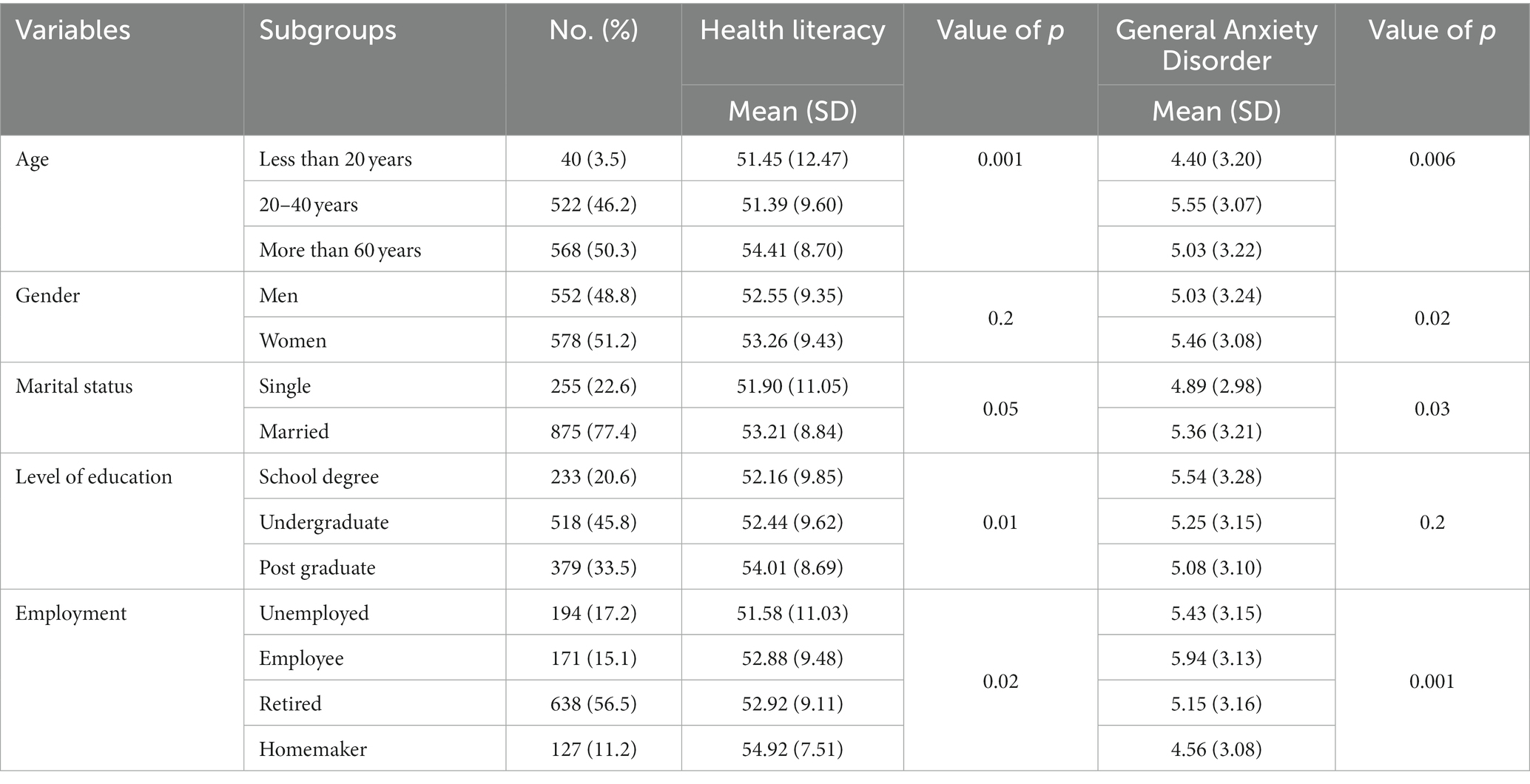
Table 1. Relationship between demographic variables and well being literacy and generalized nervousness dysfunction.
Table 1 presents the outcomes of a research investigating the connection between demographic variables (age, gender, marital standing, degree of training, and employment) and well being literacy and GAD among the many research inhabitants. The desk contains subgroups inside every variable, the quantity and proportion of individuals in every subgroup, the imply scores for well being literacy and GAD, and worth of ps indicating statistical significance.
The outcomes counsel that age had a statistically important relationship with each well being literacy and GAD, with individuals aged over 60 having the next imply well being literacy rating and decrease imply GAD rating in comparison with these aged lower than 20 or between 20–40 years previous. Gender had a statistically important relationship with GAD, with males having a decrease imply GAD rating in comparison with ladies. Marital standing was additionally discovered to have a statistically important relationship with each well being literacy and GAD, with married individuals having the next imply well being literacy rating and better imply GAD rating in comparison with single individuals. Level of training had a statistically important relationship with well being literacy however not with GAD, with postgraduate individuals having the next imply well being literacy rating in comparison with these with faculty levels or undergraduate levels. Employment standing had a statistically important relationship with each well being literacy and GAD, with retired individuals having the next imply well being literacy rating and decrease imply GAD rating in comparison with unemployed or employed individuals. Homemakers had the best imply well being literacy rating however the lowest imply GAD rating amongst all employment subgroups.
Overall, the desk offers invaluable insights into the connection between demographic variables and well being literacy and GAD among the many research inhabitants, highlighting the necessity for focused interventions to handle the distinctive wants of various subgroups.
Table 2 presents the outcomes of the affiliation between the imply (customary deviation) GAD rating, 5.25 (3.16) out of a attainable rating of 12 with a variety of scores between 1 and 12, and the imply (customary deviation) well being literacy rating, which was 52.91 (9.39) out of a attainable rating of 100 with a variety of scores between 18 and 78, amongst people aged 18–60 in Khuzestan province. The desk contains the imply scores and customary deviations for GAD and well being literacy, the worth of p, and the Pearson correlation coefficient.
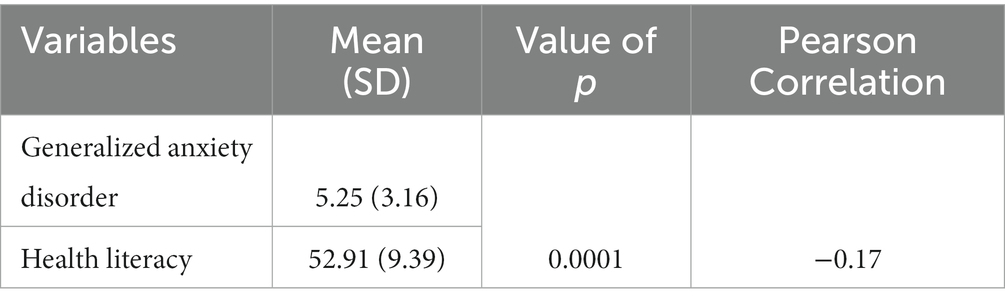
Table 2. Association between imply generalized nervousness dysfunction rating and well being literacy.
The outcomes counsel that there’s a statistically important destructive correlation between GAD and well being literacy. Specifically, as well being literacy will increase, the imply GAD rating decreases (p < 0.05). The Pearson correlation coefficient of −0.17 signifies a weak destructive correlation between these two variables. Overall, the desk offers invaluable insights into the connection between GAD and well being literacy, highlighting the significance of addressing each variables in interventions aimed toward bettering psychological well being outcomes.
Table 3 contains subgroups primarily based on the extent of well being literacy, the quantity and proportion of individuals in every subgroup, imply GAD scores with 95% vary, and worth of ps indicating statistical significance. The outcomes counsel that there’s a statistically important affiliation between the extent of well being literacy and imply GAD scores. Participants with insufficient well being literacy had the best imply GAD rating [5.8 (5.5–6.1)], adopted by these with marginal well being literacy [4.9 (4.7–5.2)]. Participants with satisfactory well being literacy had the bottom imply GAD rating [3.9 (3.1–4.6)]. The worth of ps point out statistical significance for all subgroups, suggesting that the affiliation between well being literacy and GAD is critical. The outcomes counsel that decrease ranges of well being literacy are related to larger ranges of GAD. Targeted interventions aimed toward bettering well being literacy could also be essential to handle the distinctive wants of people with insufficient or marginal well being literacy and scale back the chance of GAD.
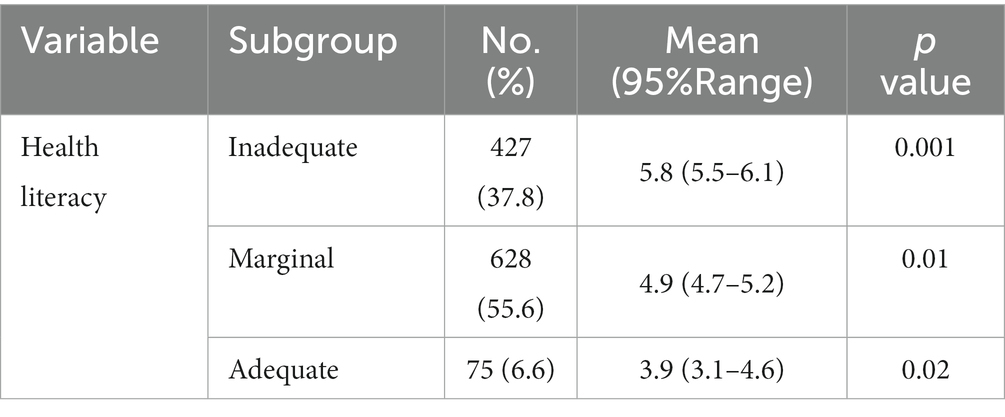
Table 3. Association between imply generalized nervousness dysfunction rating and degree of well being literacy amongst people aged 18–60 years in Khuzestan province.
Table 4 presents the outcomes that counsel that age had a statistically important relationship with well being literacy amongst ladies, with individuals aged 41–60 having the best imply well being literacy rating in comparison with different age teams (p2 < 0.05). Furthermore, there was a statistically important relationship between age and well being literacy amongst males (p1 < 0.05).
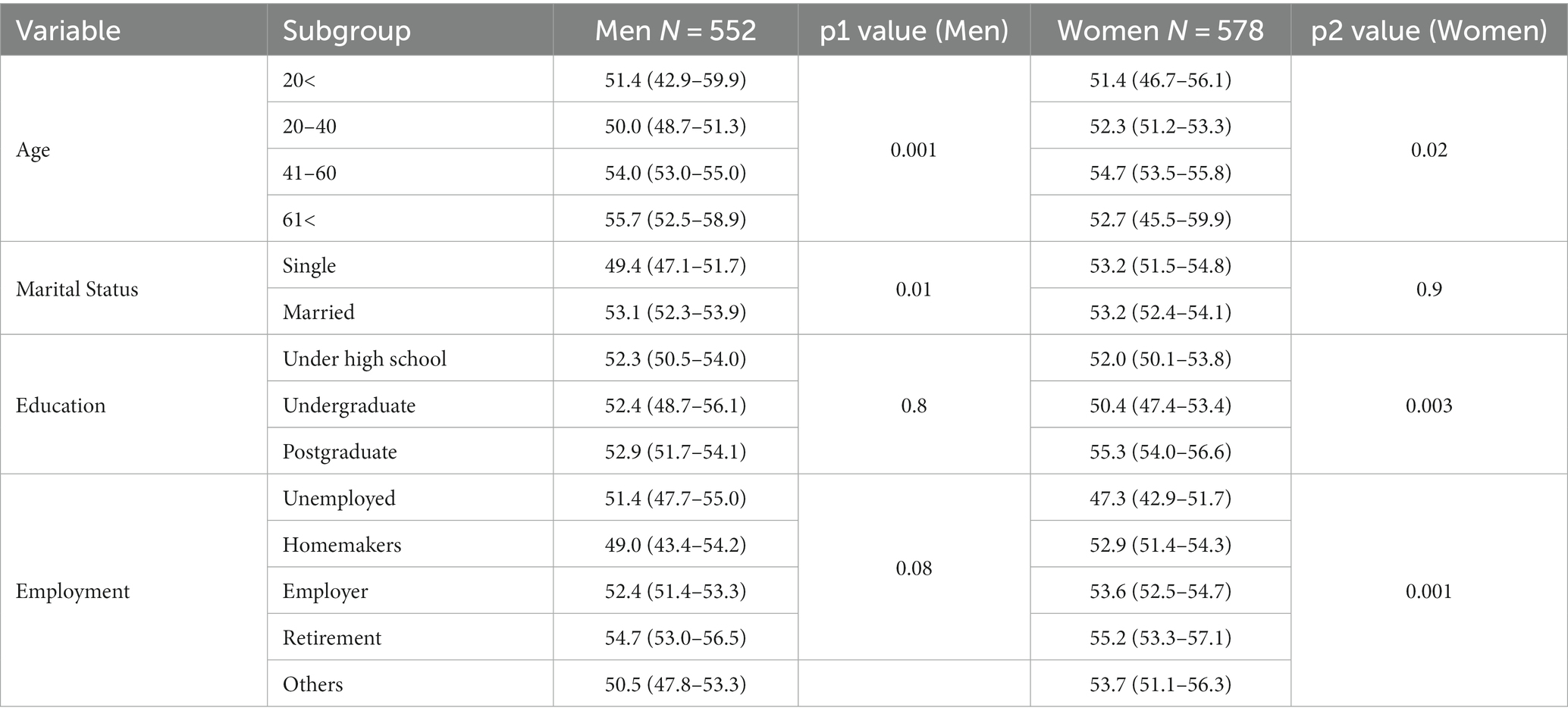
Table 4. Association between the imply rating of well being literacy and demographic variables gender-wise in Khuzestan province.
Married males had the next imply well being literacy rating in comparison with single ladies. However, there was a statistically important relationship between marital standing and well being literacy amongst males (p1 < 0.05).
Education had a statistically important relationship with well being literacy, with postgraduate ladies having the next imply well being literacy rating in comparison with these with an undergraduate diploma or below highschool training (p2 < 0.05). However, there was no statistically important relationship between training and well being literacy amongst males.
Employment had a statistically important relationship with well being literacy amongst ladies, with unemployed ladies having the bottom imply well being literacy rating in comparison with different employment (p2 < 0.05), and there was no statistically important relationship between employment and well being literacy amongst males.
The outcomes of Table 5 counsel that age had a statistically important relationship with GAD amongst ladies (p2 < 0.05), with individuals aged 20–40 having the best imply GAD rating in comparison with different age teams. However, there was no statistically important relationship between age and GAD amongst males. Marital standing had a statistically important relationship with GAD, with married ladies having the next imply GAD rating in comparison with single ladies (p2 < 0.05). However, there was no statistically important relationship between marital standing and GAD amongst males.
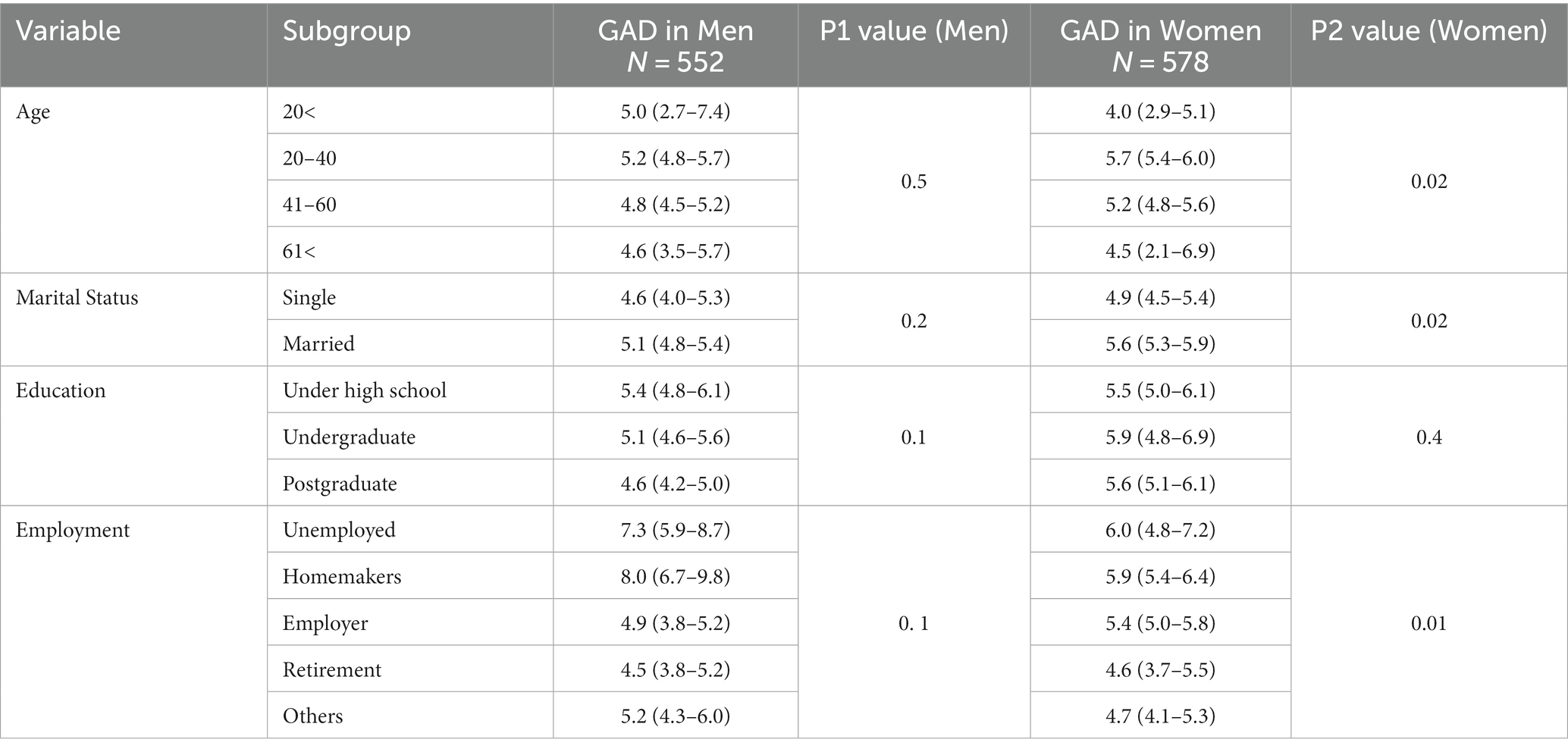
Table 5. Association between the imply rating of basic nervousness dysfunction (GAD) and demographic variables gender-wise in Khuzestan province.
Education had no statistically important relationship with GAD amongst ladies or males.
Employment had a statistically important relationship with GAD amongst ladies (p2 < 0.05), with unemployed ladies having the best imply GAD rating in comparison with different employment subgroups. However, there was no statistically important relationship between employment and GAD amongst males. Overall, the desk offers insights into the affiliation between demographic variables and GAD, particularly contemplating gender variations, in Khuzestan province. The outcomes counsel that age, marital standing, and employment could also be elements influencing GAD amongst ladies. Targeted interventions could also be essential to handle the distinctive wants of various subgroups primarily based on these demographic variables.
Discussion
Enhancing well being literacy and selling consciousness concerning COVID-19, its transmission, and preventive measures can considerably contribute to the efficient administration of tension and stress induced by the virus. This is especially essential in periods of infectious illness crises and epidemics (Paakkari and Okan, 2020). It is vital to notice that nervousness can have hostile penalties on a person’s private and social well-being, diminishing their skill to deal with bodily and psychological well being challenges and in the end resulting in a decline of their general high quality of life (Ryan and Twibell, 2000).
In this explicit research, the researchers discovered that the typical well being literacy rating among the many individuals was 9.52 ± 3.9. Additionally, the imply rating (with customary deviation) for GAD ensuing from worry of contracting COVID-19 was 2.5 ± 1.3. A big destructive correlation was noticed between the imply GAD rating and well being literacy. Furthermore, a separate research centered on kidney sufferers revealed that the imply GAD rating as a consequence of worry on this group was 13.3 ± 8.5, indicating a statistically important distinction throughout varied ranges of well being literacy among the many individuals below investigation (Qobadi et al., 2014). These findings spotlight the significance of well being literacy in relation to nervousness ranges amongst kidney sufferers.
Moreover, the outcomes of this research demonstrated a big destructive correlation between well being literacy and GAD in sufferers attending the Shahid Beheshti Polyclinic in Karaj (Shams et al., 2020). This means that people with larger ranges of well being literacy are likely to have decrease ranges of tension associated to their well being.
According to the findings of Rabiaah’s research, a big proportion of medical college students, particularly 77%, skilled stress associated to Middle East respiratory syndrome coronavirus (MERS-CoV). Among these college students, 18.4% reported at the least delicate nervousness, whereas 6.4% reported reasonable nervousness. Notably, no extreme nervousness was noticed amongst any of the scholars. The research additionally examined the typical nervousness degree ensuing from worry among the many individuals, which was measured to be 3.1 ± 2.7. This suggests a reasonable degree of tension on common among the many medical college students as a consequence of their issues about MERS-CoV (Al-Rabiaah et al., 2020).
Furthermore, the research revealed that feminine college students had larger stress ranges in comparison with their male counterparts. This signifies a gender distinction within the expertise of stress associated to MERS-CoV amongst medical college students. Additionally, the research recognized a transparent relationship between the stress ranges of medical college students and the presence of widespread nervousness dysfunction. This implies that larger stress ranges among the many college students might contribute to the event or exacerbation of tension problems.
These findings spotlight the necessity for efficient methods to handle and handle stress and nervousness amongst medical college students, notably throughout outbreaks of infectious illnesses like MERS-CoV. Providing acceptable help programs and interventions can assist mitigate the destructive influence of stress and nervousness on the well-being and tutorial efficiency of medical college students.
A research carried out by Lai et al. (2020) revealed that amongst healthcare staff offering companies to COVID-19 sufferers, the extent of tension was reported as 55.4% regular, 32.3% delicate nervousness, 7% reasonable nervousness, and 5.3% extreme nervousness. It was discovered that girls and people with direct contact with sufferers skilled larger ranges of stress.
In a separate research from South Korea throughout the MERS-CoV outbreak, it was discovered that 7.6% of quarantined people exhibited indicators of tension, whereas 16.6% skilled anger and irritability. However, after 6 months of quarantine, solely 3% of people continued to expertise nervousness, and anger and irritability have been current in solely 6.4% (Jeong et al., 2016).
According to the outcomes of one other research, 63.5% of MERS-CoV survivors suffered from extreme neurological and psychological issues. Among these people, nervousness dysfunction was noticed in 34.9%, and melancholy in 30.2%. It was famous that those that had misplaced family members throughout the epidemic, had skilled extreme sickness requiring mechanical air flow, or had pre-existing nervousness problems earlier than the virus outbreak have been extra prone to expertise these signs (Shin et al., 2019). These findings emphasize the numerous influence of infectious illness outbreaks on psychological well being, notably amongst healthcare staff and survivors. It highlights the necessity for acceptable help and interventions to handle nervousness, stress, and different psychological challenges confronted by people throughout such crises.
In the present research, the prevalence of insufficient, marginal, and satisfactory well being literacy among the many individuals was discovered to be 8.37% (427 people), 6.55% (628 people), and 6.6% (75 people), respectively. A statistically important distinction was noticed within the imply rating of GAD amongst people with totally different ranges of well being literacy. Similarly, in a separate research specializing in kidney sufferers, it was discovered that 25% had insufficient well being literacy, 8.9% had common well being literacy, and a couple of.65% had satisfactory well being literacy. There was additionally a statistically important distinction between totally different ranges of well being literacy and nervousness scores. These findings spotlight the significance of well being literacy in relation to nervousness ranges among the many topics below investigation. Adequate well being literacy seems to be related to decrease nervousness scores, emphasizing the necessity to promote and improve well being literacy as a way to tackle and handle nervousness successfully (Alizadeh Aghdam et al., 2017).
This research discovered a statistically important distinction within the imply well being literacy amongst males of various age teams and marital standing, in addition to amongst ladies of various age teams, instructional ranges, and occupational standing. However, no statistically important distinction was noticed within the well being literacy of males with totally different instructional and occupational statuses or ladies with totally different marital statuses. In one other research, a statistically important distinction was noticed between well being literacy and academic ranges. However, no statistically important distinction was discovered between well being literacy and gender, age teams, marital standing, or occupational standing.
These findings counsel that demographic elements comparable to age, gender, instructional degree, marital standing, and occupational standing might affect well being literacy ranges. Therefore, it is very important contemplate these elements when growing interventions to enhance well being literacy and promote higher well being outcomes (Alizadeh Aghdam et al., 2017).
These outcomes spotlight the gender-specific variations within the relationship between demographic variables and nervousness problems. It means that age, marital standing, and occupation might play a job in nervousness ranges amongst ladies, whereas instructional degree might not have a big influence on nervousness problems in ladies. Additionally, the research signifies that superior medical training could also be related to decrease stress and nervousness ranges amongst college students (Jeong et al., 2016). These findings contribute to a greater understanding of the elements influencing nervousness problems and may inform interventions and help methods to handle and handle nervousness successfully in several populations.
A research carried out in Iran revealed that there was no statistically important distinction within the degree of tension and stress throughout the COVID-19 pandemic amongst people primarily based on gender, age, and marital standing. However, there was a statistically important distinction primarily based on training degree (Khademian et al., 2021). These outcomes spotlight the influence of training ranges on nervousness and stress ranges among the many basic inhabitants throughout the pandemic. They additionally emphasize the numerous nervousness skilled by healthcare staff, notably in relation to their gender, age, and job place. In one other research, it was discovered that the imply rating of tension amongst healthcare staff throughout the COVID-19 outbreak had the best correlation with nervousness primarily based on gender, age, and job place, and this correlation was statistically important. Understanding these elements can assist in growing focused interventions and help programs to handle and handle nervousness successfully, each among the many basic inhabitants and healthcare staff, throughout difficult instances such because the COVID-19 pandemic (Kaveh et al., 2020).
A survey confirmed that 6.9% of academics skilled important nervousness throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. Their nervousness ranges concerning the COVID-19 epidemic have been discovered to be predictive of their age and consciousness of future curriculum planning. Specifically, older academics (aged 41–50) skilled larger ranges of tension in comparison with others. However, there was no statistically important relationship between gender and nervousness ranges associated to the illness (Ebrahimi, 2020). Based on these findings, it may be inferred that people with low well being literacy within the inhabitants of Khuzestan might expertise elevated ranges of stress, nervousness, and psychological signs throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. These outcomes spotlight the significance of addressing well being literacy and offering acceptable help and interventions to mitigate the destructive psychological influence of the pandemic on this inhabitants.
Conclusion
Limitations of the research
1. Online self-report measures: The research might have relied on self-report measures for assessing well being literacy and generalized nervousness dysfunction, which might be topic to recall bias or social desirability bias.
3. Contextual elements: The research’s findings could also be particular to the Khuzestan province in Iran and will not be generalizable to different areas or populations with totally different sociocultural contexts.
Data availability assertion
Ethics assertion
The research involving people have been authorised by Ahvaz Jundishapur University of Medical Sciences, IR.AJUMS.REC.1399.089. The research have been carried out in accordance with the native laws and institutional necessities. Written knowledgeable consent for participation on this research was supplied by the individuals.
Author contributions
AD: Data curation, Software, Writing – authentic draft. NN: Formal evaluation, Investigation, Writing – authentic draft. NH: Data curation, Project administration, Writing – authentic draft. MJ: Data curation, Project administration, Writing – authentic draft. SY: Data curation, Methodology, Writing – authentic draft. HM: Conceptualization, Writing – evaluation & modifying. MS: Conceptualization, Writing – authentic draft. MD: Software, Writing – evaluation & modifying. MC: Conceptualization, Supervision, Writing – evaluation & modifying.
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflict of curiosity
Publisher’s word
References
Alizadeh Aghdam, M. B., Koohi, Ok., and Gholizadeh, M. (2017). The relationship of self-care and well being literacy with psychological well being amongst residents of Tabriz metropolis. Health-Based Res.
Google Scholar
Al-Rabiaah, A., Temsah, M.-H., Al-Eyadhy, A. A., Hasan, G. M., Al-Zamil, F., Al-Subaie, S., et al. (2020). Middle East respiratory syndrome-Corona virus (MERS-CoV) related stress amongst medical college students at a college instructing hospital in Saudi Arabia. J. Infect. Public Health 13, 687–691. doi: 10.1016/j.jiph.2020.01.005
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Barsell, D. J., Everhart, R. S., Miadich, S. A., and Trujillo, M. A. (2018). Examining well being behaviors, well being literacy, and self-efficacy in faculty college students with continual circumstances. Am. J. Health Educ. 49, 305–311. doi: 10.1080/19325037.2018.14867
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Dodson, S., Osicka, T., Huang, L., McMahon, L. P., and Roberts, M. A. (2016). Multifaceted evaluation of well being literacy in individuals receiving dialysis: associations with psychological stress and high quality of life. J. Health Commun. 21, 91–98. doi: 10.1080/10810730.2016.1179370
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Ebrahimi, S. (2020). Evaluation of academics’ generalized nervousness dysfunction throughout the COVID-19 pandemic. J. Educ. Sci.
Google Scholar
Haghdoost, A. A., Rakhshani, F., Aarabi, M., Montazeri, A., Tavousi, M., Solimanian, A., et al. (2015). Iranian well being literacy questionnaire (IHLQ): an instrument for measuring well being literacy in Iran. Iran Red Crescent Med. J. 17:e25831. doi: 10.5812/ircmj.17(5)2015.25831
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Jeong, H., Yim, H. W., Song, Y.-J., Ki, M., Min, J.-A., Cho, J., et al. (2016). Mental well being standing of individuals remoted as a consequence of Middle East respiratory syndrome. Epidemiol. Health 38:38. doi: 10.4178/epih.e2016048
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Khademian, F., Delavari, S., Koohjani, Z., and Khademian, Z. (2021). An investigation of melancholy, nervousness, and stress and its relating elements throughout COVID-19 pandemic in Iran. BMC Public Health 21:275. doi: 10.1186/s12889-021-10329-3
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Lai, J., Ma, S., Wang, Y., Cai, Z., Hu, J., Wei, N., et al. (2020). Factors related to psychological well being outcomes amongst well being care staff uncovered to coronavirus illness 2019. JAMA Netw. Open 3:e203976.
Google Scholar
Mazza, C., Ricci, E., Biondi, S., Colasanti, M., Ferracuti, S., Napoli, C., et al. (2020). A Nationwide survey of psychological misery amongst Italian individuals throughout the COVID-19 pandemic: rapid psychological responses and related elements. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17093165
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Mohammadkhah, F., Shamsalinia, A., Shirinkam, F., Daneshnia, M., Mahmoudian, A., Rafiei, N., et al. (2021). Exploring COVID-19 nervousness in Iranian grownup primarily based on well being literacy by moderating demographic variables: a structural equation mannequin. Heliyon 7:e07336. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07336
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Nayiniyan, M., Shaeiri, M., Sharifi, M., and Hadian, M. (2011). Evaluation of the reliability and validity of the generalized nervousness Disorder-7 (GAD-7) scale. Clin. Psychol. Personal. 3, 41–50.
Google Scholar
Paulus, D. J., Wadsworth, L. P., and Hayes-Skelton, S. A. (2015). Mental well being literacy for nervousness problems: how perceptions of symptom severity would possibly relate to recognition of psychological misery. J. Public Ment. Health 14, 94–106. doi: 10.1108/JPMH-09-2013-0064
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Qobadi, M., Besharat, M. A., Rostami, R., Rahiminezhad, A., and Pourgholami, M. (2014). Health literacy, destructive emotional standing, and self-care behaviors in dialysis. J. Fundament. Mental Health 17, 46–51.
Google Scholar
Reavley, N. J., Morgan, A. J., and Jorm, A. F. (2014). Development of scales to evaluate psychological well being literacy regarding recognition of and interventions for melancholy, nervousness problems and schizophrenia/psychosis. Australian New Zealand J. Psychiatry 48, 61–69. doi: 10.1177/0004867413491157
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Ryan, M. E., and Twibell, R. S. (2000). Concerns, values, stress, coping, well being and academic outcomes of school college students who studied overseas. Int. J. Intercult. Relat. 24, 409–435. doi: 10.1016/S0147-1767(00)00014-6
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Salari, N., Hosseinian-Far, A., Jalali, R., Vaisi-Raygani, A., Rasoulpoor, S., Mohammadi, M., et al. (2020). Khaledi-Paveh B prevalence of stress, nervousness, melancholy among the many basic inhabitants throughout the COVID-19 pandemic: a scientific evaluation and meta-analysis. Glob. Health 16, 1–11. doi: 10.1186/s12992-020-00589-w
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Schulz, J. G. J., and Rapaport, M. H. (2005). The prognosis and therapy of generalized nervousness dysfunction. Prim. Psychiatry. 12, 58–67.
Google Scholar
Shams, J. H., Mohammadzadeh, Ok. A., and Maher, A. (2020). Correlation between well being literacy and high quality of life with well being nervousness in outpatient sufferers referred to Shahid Beheshti specialised polyclinic in Karaj. J. Health Promot. Manag. 9, 1–9.
Google Scholar
Shin, J., Park, H. Y., Kim, J. L., Lee, J. J., Lee, H., Lee, S. H., et al. (2019). Psychiatric morbidity of survivors one yr after the outbreak of Middle East respiratory syndrome in Korea, 2015. J. Korean Neuropsychiatr. Assoc. 58, 245–251. doi: 10.4306/jknpa.2019.58.3.245
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Vahedian-Azimi, A., Moayed, M. S., Rahimibashar, F., Shojaei, S., Ashtari, S., and Pourhoseingholi, M. A. (2020). Comparison of the severity of psychological misery amongst 4 teams of an Iranian inhabitants concerning COVID-19 pandemic. BMC Psychiatry 20, 402–407. doi: 10.1186/s12888-020-02804-9
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Von Wagner, C., Knight, Ok., Steptoe, A., and Wardle, J. (2007). Functional well being literacy and health-promoting behaviour in a nationwide pattern of British adults. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 61, 1086–1090. doi: 10.1136/jech.2006.053967
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Wang, C., Pan, R., Wan, X., Tan, Y., Xu, L., Ho, C. S., et al. (2020). Immediate psychological responses and related elements throughout the preliminary stage of the 2019 coronavirus illness (COVID-19) epidemic among the many basic inhabitants in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17:1729. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17051729
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Wolf, M. S., Gazmararian, J. A., and Baker, D. W. (2005). Health literacy and practical well being standing amongst older adults. Arch. Intern. Med. 165, 1946–1952. doi: 10.1001/archinte.165.17.1946
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Zarei, J., Badavi, M., Karandish, M., Shoushtari, M. H., Dastoorpoor, M., Yousefi, F., et al. (2021a). A research to design minimal information set of COVID-19 registry system. BMC Infect. Dis. 21:773. doi: 10.1186/s12879-021-06507-8
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
Zarei, J., Dastoorpoor, M., Jamshidnezhad, A., Cheraghi, M., and Sheikhtaheri, A. (2021b). Regional COVID-19 registry in Khuzestan, Iran: a research protocol and classes realized from a pilot implementation. Inform. Med. Unlocked 23:100520. doi: 10.1016/j.imu.2021.100520
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar


Leave a Reply