Introduction
In Iran, research have proven excessive ranges of antibiotic resistance in hospitals (10, 11), however revealed information assessing the KAP of medical residents towards AMR are absent. The current research aimed to research the medical residents’ KAP concerning antibiotics, antibiotic use and AMR in Iran to determine data gaps and tailor-made academic interventions that might result in clever use of antimicrobials and scale back the emergence of MDR organisms and their penalties.
Materials and strategies
Study design and settings
Study inhabitants
Exclusion standards
Questionnaire design
Data evaluation
Results
Demographic traits
During the research interval, out of 450 potential respondents, 400 responded and accomplished the questionnaires (response fee; 88.9%). Table 1 exhibits particulars on demographic traits of the research contributors. Their age ranged from 26 to 54 years and 227 (56.8%) contributors have been females. The imply age of respondents was 30.90 ± 3.45 years and most of them, 229 (57.2%) have been smaller or equal to 30 years. Participants have been divided into 4 teams based mostly on their subject and the yr of their college entrance, respectively. The largest group of respondents was group-1116 (29.0%), which included inside drugs, infectious, and pediatric residents. One hundred and 4 (26%) of the residents have been of their first yr of coaching, 105 (26.3%) of their second, 98 (24.6%) of their third, and 93 (23.3%) of their fourth or longer.
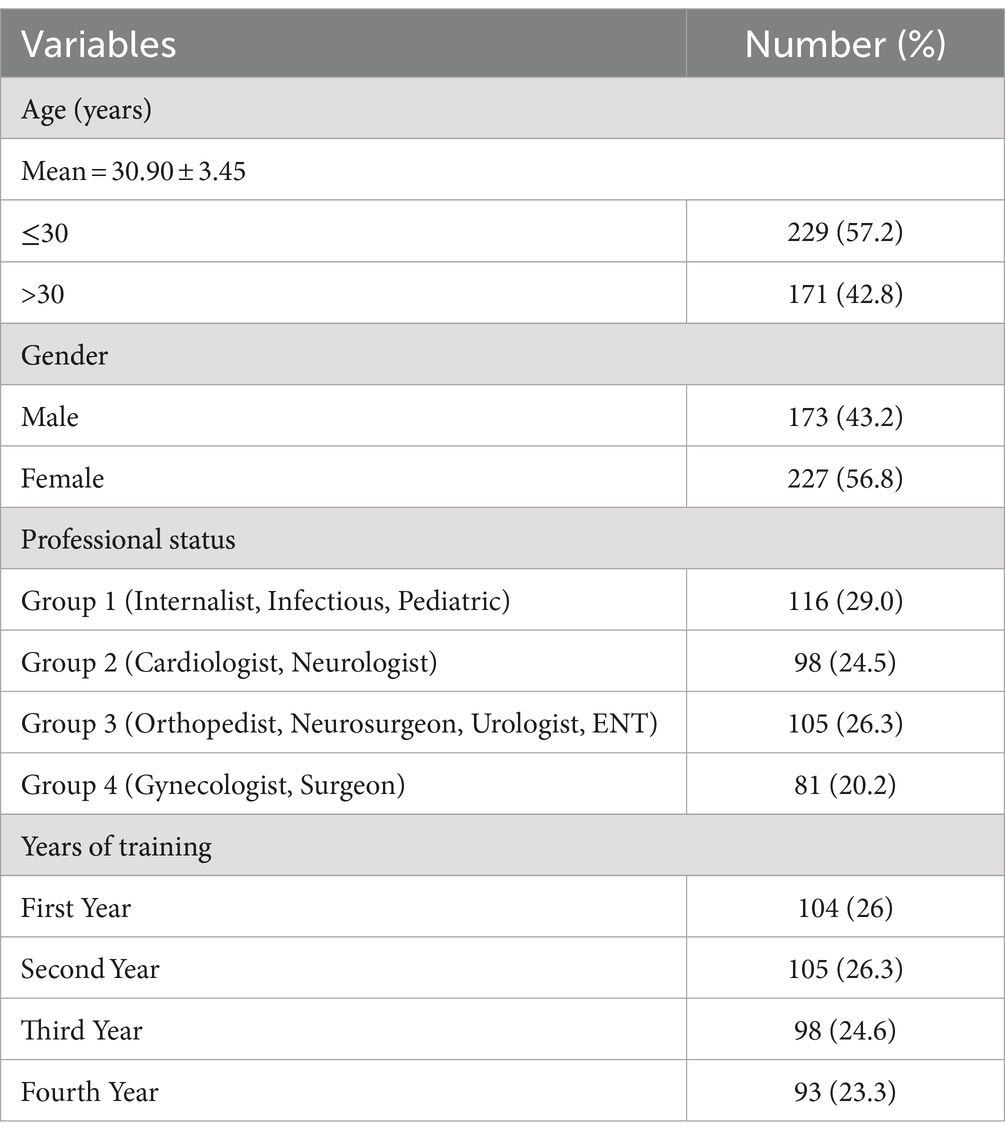
Table 1. Demographic traits of contributors (n = 400).
Medical residents’ data
Data from 11 data questions have been analyzed in response to two matters: (1) based mostly on the skilled standing of contributors, and (2) based mostly on the contributors’ years of coming into the college. The responses to data gadgets have been offered in Tables 1, 2. Overall, the typical data rating amongst contributors was 53.70 ± 15.88 in a 100-point scale. Approximately three-quarters of the contributors (293/400, 73.2%) lacked consciousness in regards to the antimicrobial stewardship program in Iran.
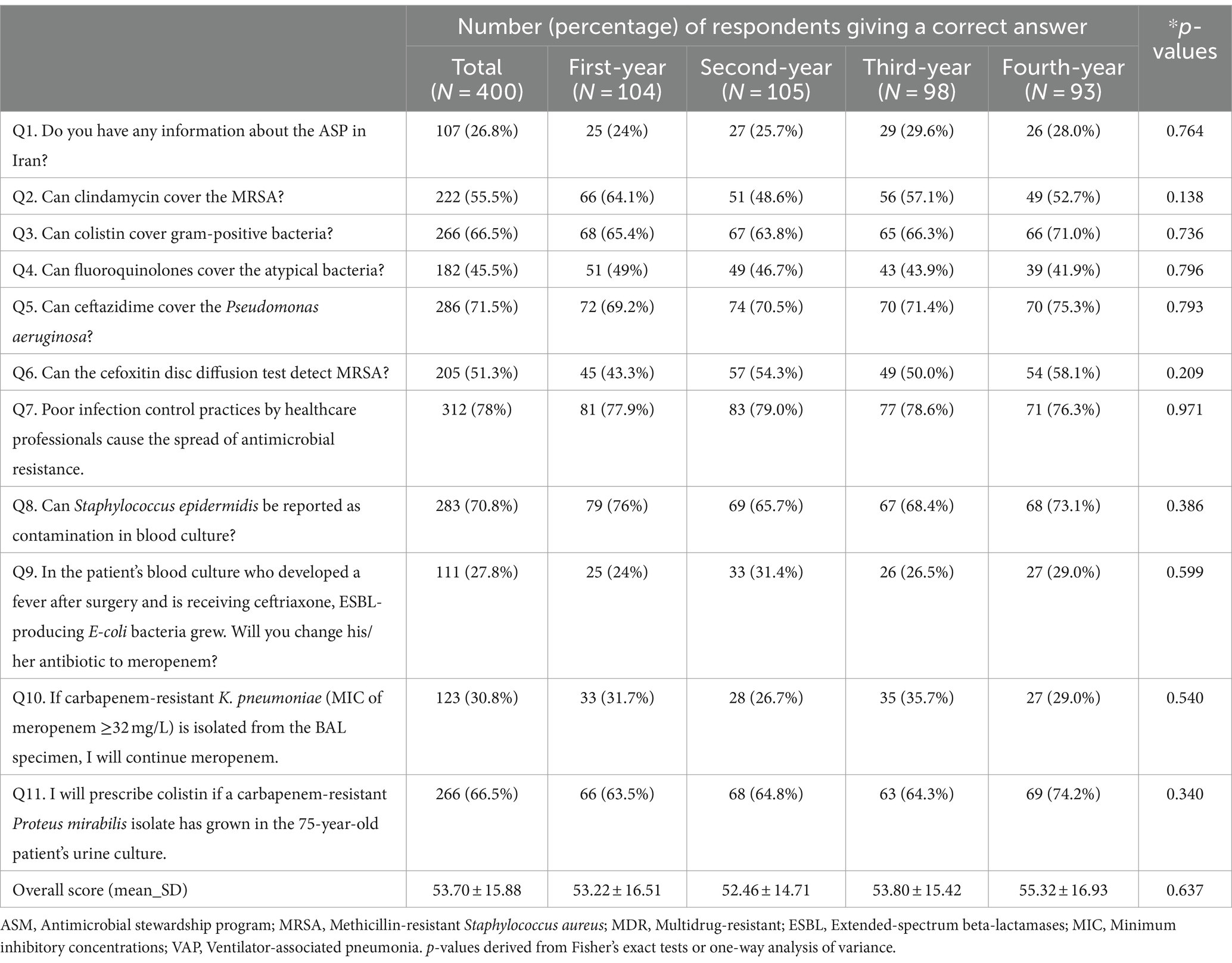
Table 2. Knowledge based mostly on the college entry yr of 400 contributors.
As it’s described in Table 3, in response to the p-values of This fall, 6 and eight, there’s a outstanding distinction between solutions of 4 teams. Regarding the query of overlaying atypical micro organism with fluoroquinolones, the very best and lowest proportion of appropriate solutions belonged to teams 1 (68/116, 58.6%) and three (30/105, 28.6%), respectively. Also, concerning using cefoxitin disc diffusion take a look at to detect methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), the bottom (35.3%) and highest (62.9%) appropriate solutions have been noticed in teams 3 and 1, respectively. A notable proportion of group 1 (87.9%) chosen the proper reply to the query about the potential of blood tradition contamination with Staphylococcus epidermidis, and the bottom proportion of appropriate solutions to this query belonged to group 4 with 55%. More than half of the contributors have been aware of the protection of colistin and its intrinsic resistance to some bacterial strains like Proteus mirabilis.
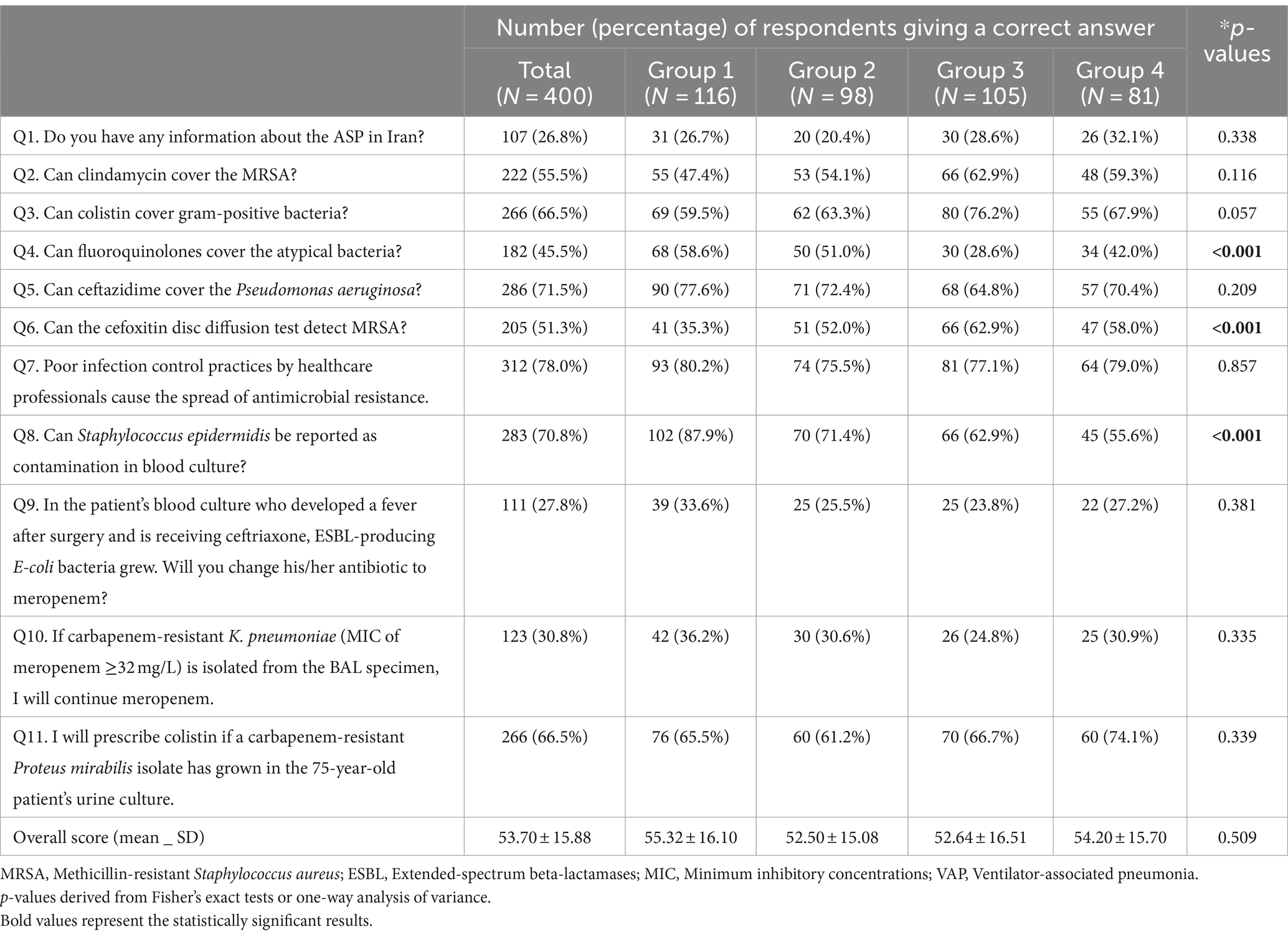
Table 3. Knowledge based mostly on skilled standing of 400 contributors.
Medical residents’ perspective
Data from 12 perspective questions have been analyzed in response to two matters: (1) based mostly on the skilled standing of contributors, and (2) based mostly on the contributors’ years of coming into the college.
Tables 4, 5 current the degrees of attitudes towards AMR and MDR organisms and ASPs among the many research contributors. The common perspective rating amongst contributors was 36.97 ± 5.89 on a 60-point scale.
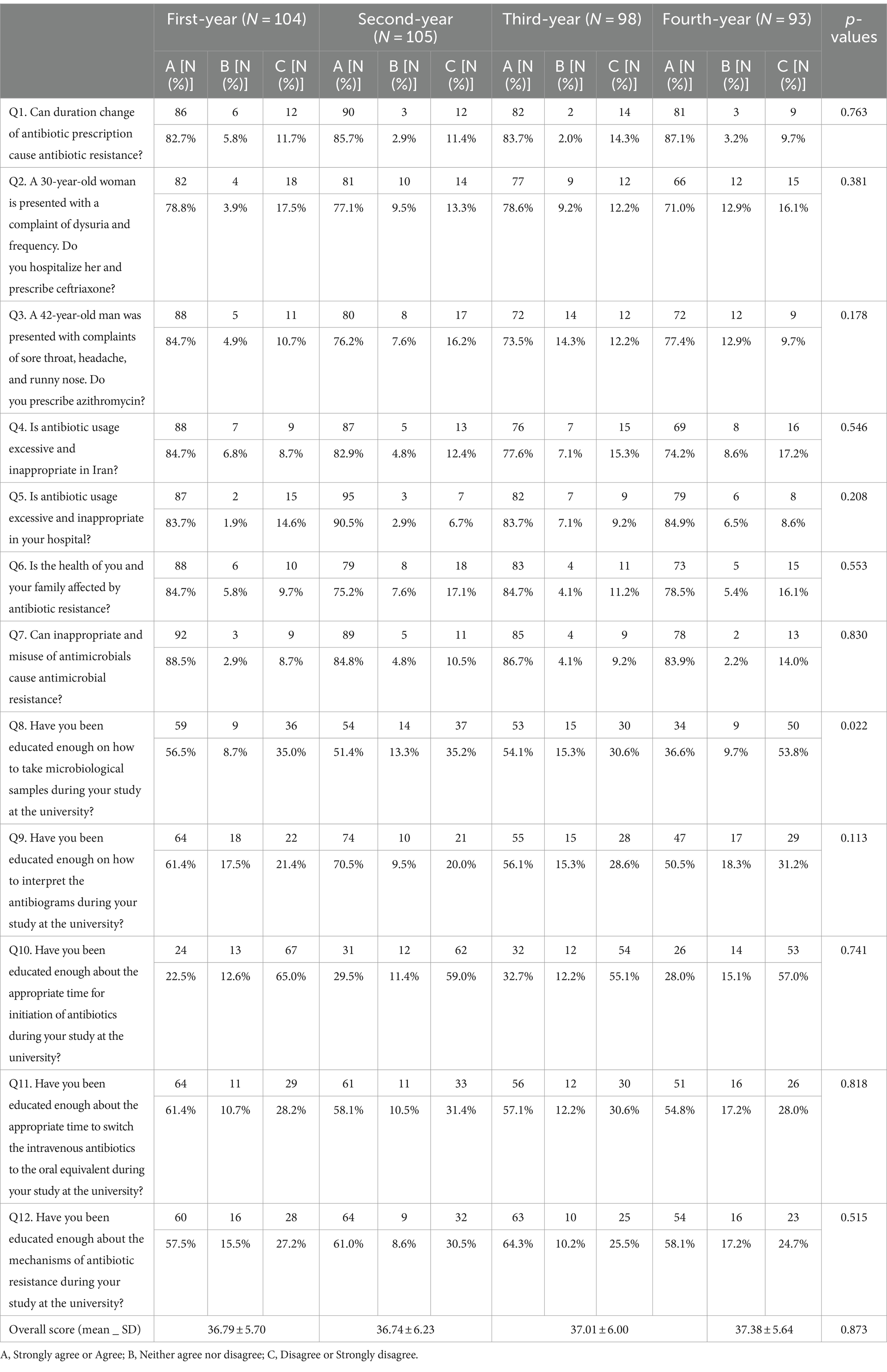
Table 4. Attitudes based mostly on the college entry yr of 400 contributors.

Table 5. Attitudes based mostly on skilled standing of 400 contributors.
Medical residents’ follow
Data from eight follow questions have been analyzed. Overall, the typical follow rating amongst contributors was 24.69 ± 4.24 on a 40-point scale. Regarding follow, 81.8% (327/400) of the respondents acknowledged that antibiotics are used to deal with flu or the frequent chilly, 78.3% (313/400) acknowledged that antibiotics ought to be discontinued when signs disappear, 58.8% acknowledged that they prescribe antibiotics due to the affected person’s insistence, 62.3% (249/400) acknowledged that they prescribe antibiotics in response to the rules, 71.3% (285/400) acknowledged that they prescribe antibiotics earlier than getting ready the microbiology tradition outcomes based mostly on the native antibiotic resistance sample, 65% (260/400) acknowledged that earlier than altering antibiotics, they differentiate colonization from an infection based mostly on the outcomes of microbial tradition, 80.3% (321/400) acknowledged that earlier than the antibiotic change, based mostly on antibiogram end result, they take note of the sorts of antibiotics the affected person obtained beforehand and 70.5% they seek the advice of with infectious illness specialists to utilizing of broad-spectrum antibiotics.
Table 6 exhibits solely query 8 has a p-value <0.05 and so on this query, there’s a vital distinction between solutions of various years of coaching. As proven in Table 7, questions 1, 2, 4, and eight have p-value<0.05 and so in these questions there are vital variations between solutions of various teams.
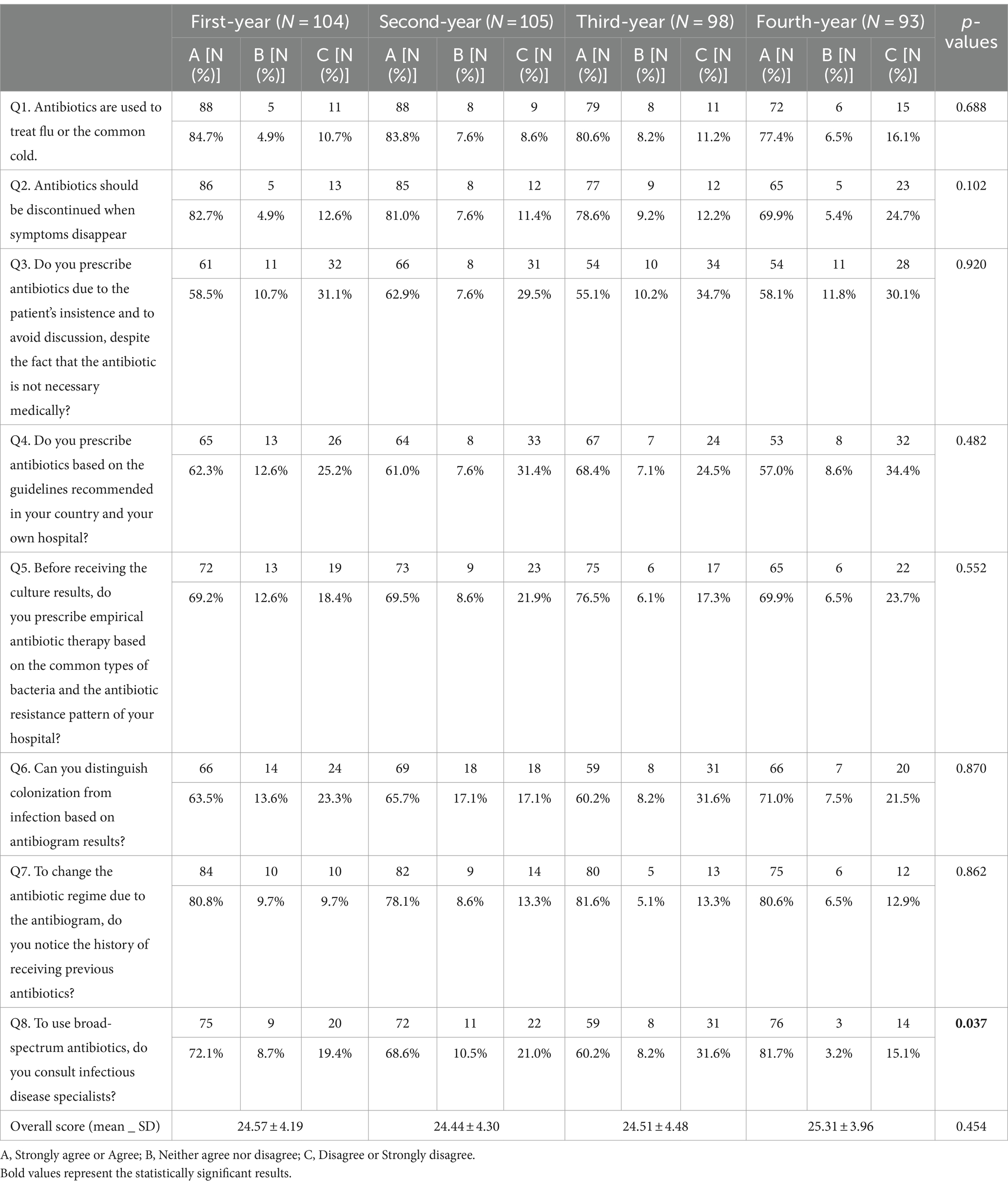
Table 6. Practices based mostly on the college entry yr of 400 contributors.
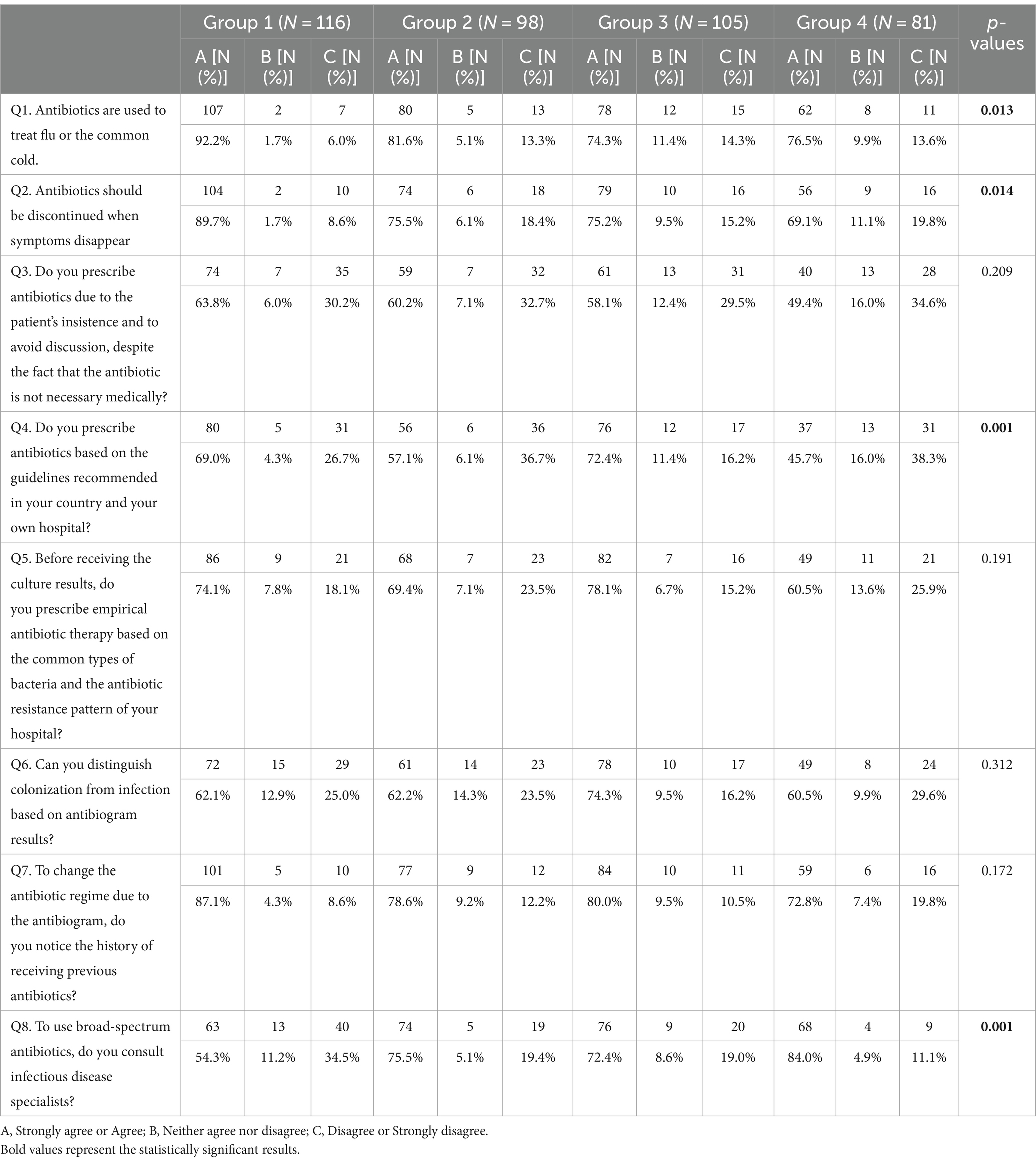
Table 7. Practices based mostly on skilled standing of 400 contributors.
Discussion
The improve in AMR is a significant risk to public well being within the twenty first century. Medical professionals are the important thing stakeholders within the prevention and management of AMR by way of strict and efficient prescribing practices, selling consciousness of ASPs and antibiotic resistance mechanisms, in addition to they’re the cornerstone of fine well being programs.
Although data of the ASPs is critical for the residents, the vast majority of our respondents (73.2%) declared that they didn’t know what antimicrobial stewardship meant and it was not taught through the 4 years of their research as a result of the data has not modified in years. The common age of our statistical inhabitants was 30.9-year-old physicians who labored in hospitals and clinics earlier than beginning residency and sadly, regardless of working within the scientific surroundings, they didn’t know this system. The gaps recognized in data amongst our residents concerning ASPs require heightened academic interventions and these actions may very well be focused. Therefore, we really helpful reinforcing the curriculum by introducing extra lectures on ASPs. Some nations, corresponding to France, the United States and Scotland, have developed a nationwide suggestions program to enhance antibiotic stewardship of their nations (4).
Amazingly, solely 45.5% of the respondents answered appropriately that quinolones present distinctive protection towards atypical pathogens. Notably, 28.6% of group 3 have been conscious that fluoroquinolones can cowl the atypical micro organism, which could be very low in comparison with different teams. It was anticipated that the data would improve based mostly on the years of training and that the primary group in comparison with different teams can be completely different because of their each day involvement with antibiotics. Low ranges of information in regards to the levofloxacin spectrum have been documented among the many clinicians in Pakistan and solely 20% appropriately recognized it to be efficient towards atypical micro organism (4). Our end result revealed that there have been no vital variations within the data among the many residents based mostly on the skilled standing of contributors and contributors’ years of coming into the college. This might be as a result of lack of AMR data switch from professors to residents. In reality, the data switch chain is incomplete as a result of these identical residents turn into professors after commencement.
MRSA is a crucial human pathogen that causes all kinds of community-and well being care-associated infections. Accuracy and promptness within the detection of meticillin resistance utilizing disk diffusion testing with oxacillin or cefoxitin are of elementary significance in guaranteeing appropriate antibiotic therapy in sufferers and management of MRSA within the hospital (18). The outcomes of our research confirmed that solely 51.3% of our residents knew that cefoxitin disc is used to determine micro organism.
In our research, the vast majority of respondents 80 and 85.8% acknowledged that antibiotics have been used inappropriately in Iran and their office hospitals, respectively. This is in step with earlier research (20, 21). In distinction, in Ghana, the vast majority of the respondent physicians answered that antibiotics have been used appropriately of their models or departments (13).
Regarding the data, the research discovered that almost all of the inhabitants (80.8%) acknowledged that antibiotic resistance can influence their well being and that of their households. An analogous discovering was present in a research performed among the many public in Cyprus, the place 76.4% of respondents have been involved in regards to the influence of resistance on the well being of people and their households (24). Interestingly, the vast majority of our residents (72%) agreed that they didn’t get the required details about the precise time to prescribe antibiotics throughout their college programs. Therefore, these outcomes confirmed that there’s a lack of enough coaching on antibiotic prescribing throughout training and pharmaceutical promotional actions in Iranian universities. It appears that prescribing antibiotics is a priority for residents and the necessity for infectious session to prescribe is felt, and so they additionally attempt to use nationwide and hospital tips.
Our research has some potential limitations. At first, it was performed solely on the Medical University of Isfahan and will not be a consultant pattern. Secondly, as with most surveys, there’s the chance that respondent residents obtained solutions to among the data questions by way of Internet searches or literature critiques. Because in actuality, it appears that evidently their data about some questions is lower than the reported values.
Conclusion
The current research highlighted the gaps in data, perspective and practices of the residents concerning AMR, ASPs and MDR pathogens. The general common data rating amongst residents was 53.70 ± 15.88. Group 1, which is the principle antibiotic prescribing group, had a mean rating of 55.32 ± 16.10, which was not considerably completely different from the opposite three teams. As nicely, based mostly on the yr of coming into the college, we see that the residents’ data (Table 2) and perspective (Table 4) in regards to the talked about matters doesn’t improve throughout 4 years, even in some instances, the data has decreased. These findings point out that training and intervention actions together with reviewing the curricula and introducing the course of mechanisms of antibiotic resistance and ASPs in residents’ curricula are essential to extend data, promote accountable antibiotic use, and fight the rising risk of AMR.
Data availability assertion
Ethics assertion
Author contributions
FK: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal evaluation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Validation, Visualization, Writing – unique draft, Writing – assessment & modifying. GS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – unique draft, Writing – assessment & modifying. NM: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal evaluation, Investigation, Methodology, Software, Writing – unique draft, Writing – assessment & modifying. MS: Methodology, Validation, Writing – unique draft, Writing – assessment & modifying. HS: Conceptualization, Data curation, Formal evaluation, Funding acquisition, Investigation, Methodology, Project administration, Resources, Software, Supervision, Validation, Visualization, Writing – unique draft, Writing – assessment & modifying.
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflict of curiosity
Publisher’s observe
References
1. Touat, M, Brun-Buisson, C, Opatowski, M, Salomon, J, Guillemot, D, Tuppin, P, et al. Costs and outcomes of 1-year post-discharge care trajectories of sufferers admitted with an infection because of antibiotic-resistant micro organism. J Inf Secur. (2021) 82:339–45. doi: 10.1016/j.jinf.2021.02.001
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
2. O’Neill, J, and Grande-Bretagne,. Antimicrobial resistance: tackling a disaster for the well being and wealth of countries; the assessment on antimicrobial resistance: London, UK. J Antimicrobial Resistance. (2014)
Google Scholar
3. Precha, N, Sukmai, S, Hengbaru, M, Chekoh, M, Laohaprapanon, S, Makkaew, P, et al. Knowledge, attitudes, and practices concerning antibiotic use and resistance amongst well being science and non-health science college college students in Thailand. PLoS One. (2024) 19:e0296822. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0296822
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
5. Browne, AJ, Chipeta, MG, Haines-Woodhouse, G, Kumaran, EPA, Hamadani, BHK, Zaraa, S, et al. Global antibiotic consumption and utilization in people, 2000-18: a spatial modelling research. Lancet Planet Health. (2021) 5:e893–904. doi: 10.1016/S2542-5196(21)00280-1
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
8. Min, S, Zhou, Y, Sun, Y, Ye, J, Dong, Y, Wang, X, et al. Knowledge, perspective, and follow related to antimicrobial resistance amongst medical college students between 2017 and 2022: a survey in East China. Front Public Health. (2022) 10:1010582. doi: 10.3389/fpubh.2022.1010582
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
9. Lagadinou, M, Tsami, E, Deligakis, A, Paraskevas, T, Michailides, C, Velissaris, D, et al. Knowledge and attitudes of healthcare employees in the direction of antibiotic use and antimicrobial resistance in two main tertiary hospitals in Western Greece. Antibiotics (Basel). (2023) 12:1–9. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12111583
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
10. Sanikhani, R, Akbari, M, Hosseinzadeh, M, Siavash, M, Badmasti, F, and Solgi, H. Outbreak of colistin and carbapenem-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae ST16 co-producing NDM-1 and OXA-48 isolates in an Iranian hospital. BMC Microbiol. (2024) 24:59. doi: 10.1186/s12866-024-03207-6
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
11. Khoshbakht, R, Kabiri, M, Neshani, A, Khaksari, MN, Sadrzadeh, SM, Mousavi, SM, et al. Assessment of antibiotic resistance adjustments through the Covid-19 pandemic in northeast of Iran throughout 2020–2022: an epidemiological research. Antimicrob Resist Infect Control. (2022) 11:121. doi: 10.1186/s13756-022-01159-y
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
12. Liu, C, Liu, C, Wang, D, and Zhang, X. Knowledge, attitudes and intentions to prescribe antibiotics: a structural equation modeling research of major care establishments in Hubei, China. Int J Environ Res Public Health. (2019) 16:1–16. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16132385
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
13. Labi, AK, Obeng-Nkrumah, N, Bjerrum, S, Aryee, NAA, Ofori-Adjei, YA, Yawson, AE, et al. Physicians’ data, attitudes, and perceptions regarding antibiotic resistance: a survey in a Ghanaian tertiary care hospital. BMC Health Serv Res. (2018) 18:126. doi: 10.1186/s12913-018-2899-y
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
14. Nisabwe, L, Brice, H, Umuhire, MC, Gwira, O, Harelimana, JD, Nzeyimana, Z, et al. Knowledge and attitudes in the direction of antibiotic use and resistance amongst undergraduate healthcare college students at University of Rwanda. J Pharm Policy Pract. (2020) 13:7. doi: 10.1186/s40545-020-00207-5
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
15. Abbo, L, Sinkowitz-Cochran, R, Smith, L, Ariza-Heredia, E, Gómez-Marín, O, Srinivasan, A, et al. Faculty and resident physicians’ attitudes, perceptions, and data about antimicrobial use and resistance. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol. (2011) 32:714–8. doi: 10.1086/660761
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
16. Navarro-San Francisco, C, Del Toro, MD, Cobo, J, De Gea-García, JH, Vañó-Galván, S, Moreno-Ramos, F, et al. Knowledge and perceptions of junior and senior Spanish resident medical doctors about antibiotic use and resistance: outcomes of a multicenter survey. Enferm Infecc Microbiol Clin. (2013) 31:199–204. doi: 10.1016/j.eimc.2012.05.016
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
17. Khan, AKA, and Banu, G. Antibiotic resistance and usage-a survey on the data, perspective, perceptions and practices among the many medical college students of a southern Indian educating hospital. J Clin Diagn Res. (2013) 7:1613–6. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2013/6290.3230
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
18. Bonjean, M, Hodille, E, Dumitrescu, O, Dupieux, C, Nkoud Mongo, C, Allam, C, et al. Disk diffusion testing for detection of methicillin-resistant staphylococci: does Moxalactam enhance upon Cefoxitin? J Clin Microbiol. (2016) 54:2905–9. doi: 10.1128/JCM.01195-16
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
19. Dargère, S, Cormier, H, and Verdon, R. Contaminants in blood cultures: significance, implications, interpretation and prevention. Clin Microbiol Infect. (2018) 24:964–9. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2018.03.030
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
20. Marzan, M, Islam, DZ, Lugova, H, Krishnapillai, A, Haque, M, and Islam, S. Knowledge, attitudes, and practices of antimicrobial makes use of and resistance amongst public college college students in Bangladesh. Infect Drug Resist. (2021) 14:519–33. doi: 10.2147/IDR.S289964
PubMed Abstract | Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
21. Mudenda, S, Chisha, P, Chabalenge, B, Daka, V, Mfune, RL, Kasanga, M, et al. Antimicrobial stewardship: data, attitudes and practices concerning antimicrobial use and resistance amongst non-healthcare college students on the University of Zambia. JAC Antimicrob Resist. (2023) 5:1–10. doi: 10.1093/jacamr/dlad116
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar
24. Michaelidou, M, Karageorgos, SA, and Tsioutis, C. Antibiotic use and antibiotic resistance: public consciousness survey within the Republic of Cyprus. Antibiotics (Basel). (2020) 9:1–13. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics9110759
Crossref Full Text | Google Scholar

