Highlights
– Ahvaz metropolis is among the most polluted cities within the Middle East and the world.
– PM10, NO2, SO2 and O3 considerably elevated cardiovascular hospital admissions amongst human.
– Data proven right here could encourage additional research would permit assessing the event in well being standing extra exactly.
– Air air pollution has had hazardous cardiovascular results in Ahvaz metropolis.
Introduction
In current years, the manufacturing and emission of air pollution on account of extreme local weather change, the uncontrolled improve of urbanization, rising consumerism, excessive waste manufacturing, lowering rainfall, rising desertification, on account of the prevalence of mud phenomenon, the conversion of forest areas into agricultural fields, rising air pollution from trade and rising emissions from transportation have been among the many most severe issues. These elements trigger heavy injury to human societies by rising the variety of hospitalizations and the price of therapy, rising the variety of deaths, and intensification of financial and social injury brought on by closures on account of air air pollution occasions (1, 2). The most vital influencing elements are the sort, measurement, and focus of inhaled pollution (3). Man-made pollution are emitted from mounted sources (corresponding to energy crops, petrochemicals, chemical crops) and cellular sources (together with transportation, automobiles, plane, trains, and development of individuals) that improve the chance of illness in people (4–6).
Respiratory ailments, pulmonary ailments, cardiovascular ailments, and deaths as a result of excessive focus of air pollution and deeper penetration into the respiratory system are the primary problems for human well being (7, 8). In each developed and creating international locations in current many years, air air pollution (floor stage of ozone, nitrogen dioxide, sulfide dioxide, and particle matter) has grow to be one of the vital elements that trigger many well being results corresponding to bronchial asthma, bronchitis, respiratory and heart problems, and totally different cancers (abdomen, blood, liver, lung, kidney, mind) and dying (7). Based on a report by the World Health Organization (WHO) and one other well being group, ~6.4 million individuals have Disability-Adjusted Life Year (DALY) and seven million individuals have died on account of publicity to pollution in indoor and outside air (9–11). The essential elements that decide the severity of well being penalties rely on the focus of pollution in ambient air and the length of publicity to polluted air (12, 13). The most vital method air pollution enter the physique are by the respiratory system, digestion, swallowing, pores and skin, nasal mucosa, and eyes, which trigger numerous ailments together with cataracts, pores and skin ailments (itching, redness, and dry pores and skin), heart problems, the higher and decrease respiratory system, gastrointestinal ailments, numerous cancers (abdomen, intestines, mind, lungs, ovaries, and prostate), infertility and undesirable abortion, particularly in teams delicate to air air pollution (youngsters, the aged, coronary heart and respiratory sufferers) and finally dying (4, 14–16).
The focus and variety of pollution are influenced by a number of parameters corresponding to aerosol composition, aerosol cost, particle dryness, division energy, wind velocity, and sampling quantity (17). Exposure to air pollution throughout train has extra damaging results on lung well being on account of larger publicity to pollution. Decreasing using fossil fuels, modifying the commercial manufacturing course of, bettering the gasoline high quality of conveyors and rising public transportation may be efficient in diminishing the detrimental results on the financial system and well being due to inhaling air pollution. If the strategies are adopted correctly and severely, it’s doable to stop the inhalation of polluted air, which may trigger plenty of harmful and irreparable injury to the surroundings, animals, and people (18). Extreme train will increase the variety of breaths per minute. In many circumstances, athletes breathe by the mouth as an alternative of the nostril when exercising, that means that many air pollution corresponding to bioaerosols can simply penetrate the lungs (19).
The essential dangers that threaten the surroundings, animal, and human well being embrace fast inhabitants development, wastewater, local weather change, mud storms, and the event of industries corresponding to petroleum, gasoline, oil, and metal in areas of Iran (20). This examine aimed to analyze the implications of publicity to ozone, nitrogen dioxide, particle matter, and sulfide dioxide and consider cardiovascular mortality, hospital admission respiratory illness, and hospital admission heart problems in Ahvaz megacity from 2010 to 2014.
Materials and Methods
Study Design

Table 1. Criteria air pollution concentrations (μg/m3) and Health results evaluation of CAP on Ahvaz megacity inhabitants, 2010-2014.
Ahvaz with an space of 185 km2 on the middle of Khuzestan province, positioned within the southwest of Iran and to the north of the Persian Gulf, positioned at 31° 19′ 13″ N, 48° 40′ 9″ E. Ahvaz is among the largest cities in Iran (26). The inhabitants of Ahvaz is 1,300,000. The local weather is heat more often than not, with heat summers and lengthy and reasonable winters, and temperatures reaching as excessive as 50°C. The land space is 140 km2 (27). PM10, O3, NO2, and SO2 information from the Department of Environment and Meteorological Organization had been collected from the Deputy of Health (Ahvaz metropolis). Based on these standards, 4 monitoring stations had been chosen. The geographical location of the world below examine (Ahvaz metropolis) is proven in Figure 1.
Figure 1. Located of sampling stations in Ahvaz megacity.
Air Q Software
Quantification of PM10, O3, NO2, and SO2 pollution for well being impression evaluation (HIA) was carried out by using Air Q modeling software program.
Air Q software program consists of two fashions of quantification and life tables. These life tables and well being results had been used on this examine. Population contact information together with demographics, well being outcomes, and air high quality information had been fed into the software program. The relative danger (RR) in formulation 1 was used to calculate the Attributable proportion (AP) worth (4, 27–29).
AP = ∑([RR(c)−1]*P(c)])/∑[RR(c)*P(c)] (1)
In which AP is the same as the proportion of the inhabitants uncovered to the pollutant over a specified time frame (attributed ratio), RR (c) is the relative danger of well being results on the goal inhabitants within the contact group c and P (c) equals the inhabitants ratio of the publicity group c.
The variety of circumstances per 100,000 inhabitants in danger (BE) may be calculated by Formula 2.
B represents the variety of well being outcomes per 100,000 populations in danger. Due to the inaccessibility of hospital information, baseline incidence (BI) values had been used from different research (28, 30, 31). AP can calculate by the next formulation (32):
IE = I× AP (3)
The whole variety of circumstances attributable (NE) was calculated utilizing Formula 4 to judge the well being results on the variety of at-risk populations (N) (proven in Table 1).
Data Collection
The current examine is an epidemiological examine that correlated the focus of PM10, O3, NO2, and SO2 to the variety of CM, HARD, and HACD throughout the interval 2010-2014. The hourly concentrations of CAP had been obtained from the Department of Environment (DOE) Ahvaz.
Classification of well being endpoint on this examine relies on the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10) indication for whole mortality (TM- J95.150), hospital admission respiratory illness (HARD- J44.8), hospital admission heart problems (HACD- I51.6), and cardiovascular mortality (CM- I25.8) (33–35). The well being impact on this examine was investigated with used baseline incidence, relative danger, and proportion attributed to CAP by the Air-Q mannequin.
Results
Investigation of cardiovascular mortality, hospital admission heart problems, hospital admission respiratory illness and the connection between standards air pollution and wishes to assemble data uncovered inhabitants and focus of O3, PM10, SO2, and NO2.
Table 1 exhibits the variety of well being endpoints associated to the standards air pollutant concentrations on Ahvaz residents throughout 2010-2014. It exhibits that the development of yearly focus of particle matter was decreased and associated to ozone and that nitrogen dioxide and sulfide dioxide elevated throughout 2010-2014.
As proven in Table 1, the extent of sulfide dioxide, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone in 2013 was at a most. In this examine central relative danger based on sulfide dioxide, particle matter, nitrogen dioxide, and ozone had been used to calculate the variety of circumstances (Table 1).
Based on the outcome, the annual stage of CAP throughout the identical interval had been SO2: 78.92, 91.07, 92.75, 112.3, and 88.57 μg/m3; NO2: 28.7, 31, 37, 41, and 34 μg/m3; PM10: 281.98, 288.38, 278.12, 242.29, and 205.52 μg/m3; O3: 66.52, 72.67, 102.27, 223, and 187 μg/m3, respectively.
Finding confirmed that, the variety of CM attributed to particle mater had been (478, 506, 469, 427, and 371); ozone (19, 24, 43, 56, and 49); nitrogen dioxide (18, 20, 23, 27, and 21); and sulfide dioxide (26, 31, 37, 43, and 11), in 2010 till 2014, respectively (Table 1). The variety of HARD attributed to PM had been (2,054, 2,277, 2,675, 2,042, and 1,895); O3 (27, 35, 58, 73, and 63); NO2 (23, 24, 15, 25, and 18); and SO2 (23, 24, 25, 30, and 20), throughout 2010-2014, respectively (Table 1).
Table 1 exhibits that the variety of HACD associated to particle mater had been (560, 586, 529, 503, and 472); ozone (22, 32, 38, 55, and 51); nitrogen dioxide (19, 18, 13, 21, and 14); and sulfide dioxide (12, 14, 16, 22, and 9), in 2010 till 2014, respectively.
Figure 2 presents the annual common of the standards air pollution in ambient air of Ahvaz City, Iran. As depicted in Figure 2, particle matter was a reducing development and different pollution together with ozone, sulfide dioxide and nitrogen dioxide had an rising after which a reducing development.
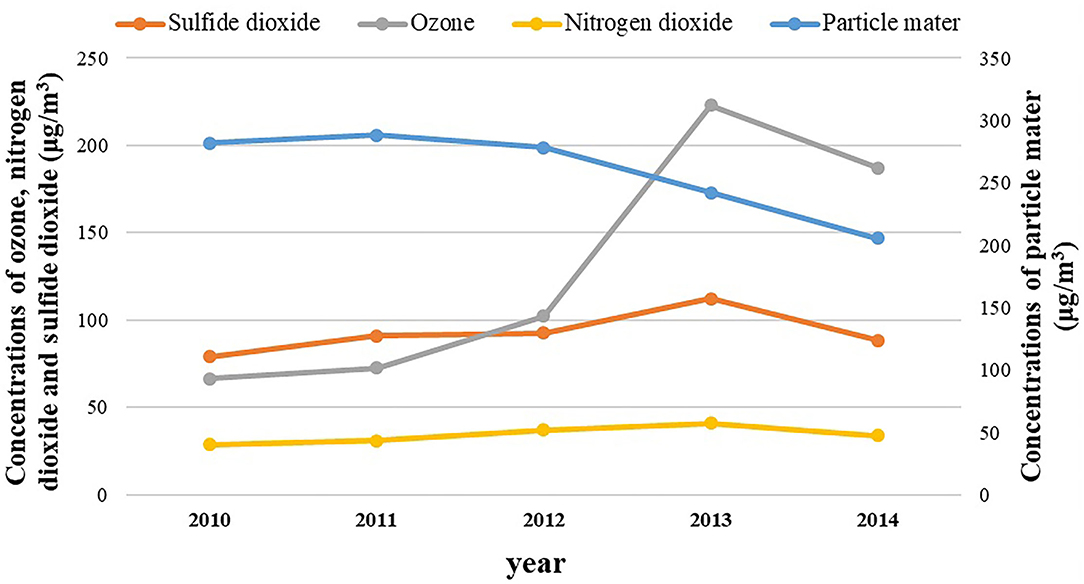
Figure 2. Annual averages of the standards air pollution throughout the examine interval in ambient air of Ahvaz City, Iran.
The cumulative variety of cardiovascular mortality, hospital admission respiratory illness, hospital admission heart problems associated to standards air pollution throughout 2010 to 2014 is illustrated in Figure 3. Figure 3 exhibits that the variety of well being endpoints of publicity to standards air pollution had been characterised by a sinusoidal course of (first rising after which reducing).
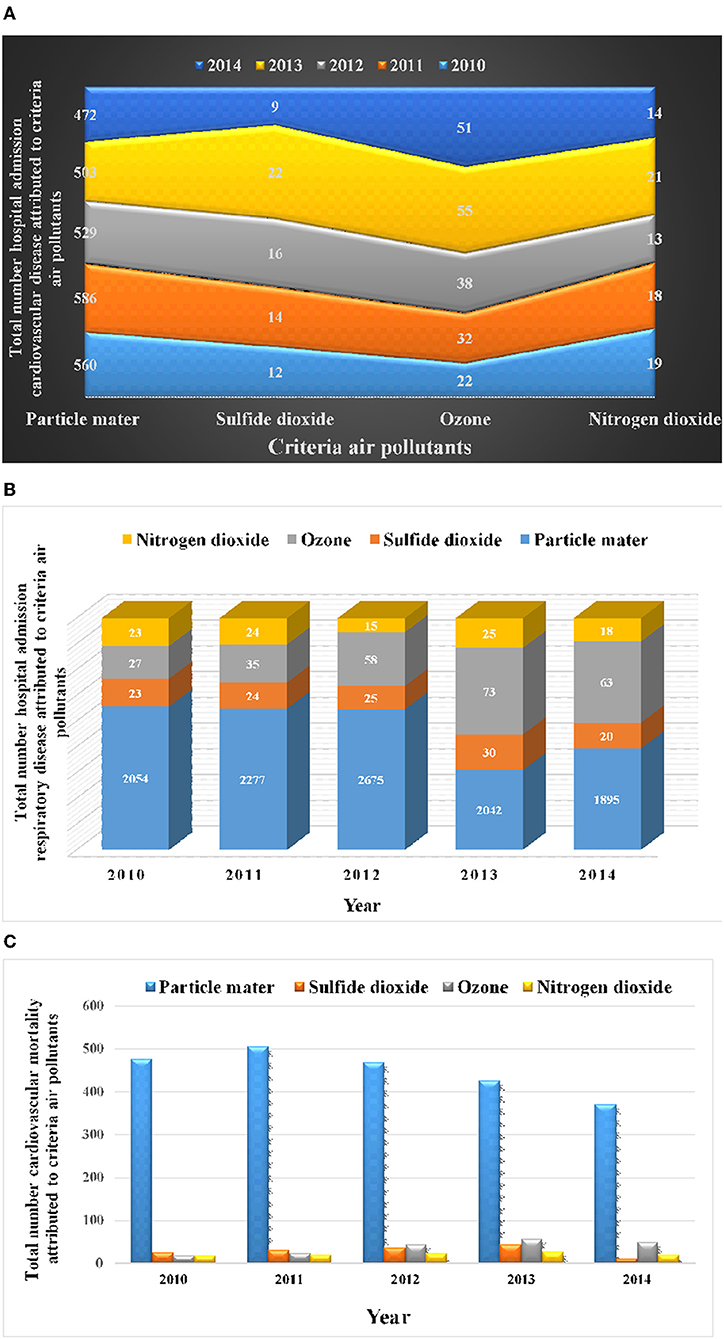
Figure 3. Cumulative variety of cardiovascular mortality, hospital admission respiratory illness, hospital admission heart problems associated to standards air pollution. (A) Number of hospital admission heart problems. (B) Number of hospital admission respiratory illness. (C) Number of cardiovascular mortality.
Discussion
Recently the disadvantages of ozone, nitrogen dioxide, particle matter, and sulfide dioxide on bodily and psychological well being have attracted the eye of many researchers. According to the results of this examine most circumstances of CM, HACD and HARD had been associated to O3, PM10, SO2, and NO2 throughout the yr 2013. The outcomes additionally confirmed that the best calculated variety of circumstances well being endpoint concerning PM10 was from 2010 to 2011.
Based on these findings, the annual stage of common ozone, nitrogen dioxide, particle mater and sulfide dioxide concentrations throughout the identical interval had been 66.52, 72.67, 102.27, 223, and 187 μg/m3; 28.7, 31, 37, 41, and 34 μg/m3; 281.98, 288.38, 278.12, 242.29, and 205.52 μg/m3; 78.92, 91.07, 92.75, 112.3, and 88.57 μg/m3, respectively.
These outcomes indicated that the variety of CM attributed to particle mater had been (478, 506, 469, 427, and 371); ozone (19, 24, 43, 56, and 49); nitrogen dioxide (18, 20, 23, 27 and 21); and sulfide dioxide (26, 31, 37, 43, and 11), within the years 2010 to 2014, respectively. The variety of HACD associated to particle mater had been (560, 586, 529, 503, and 472); ozone (22, 32, 38, 55, and 51); nitrogen dioxide (19, 18, 13, 21, and 14); and sulfide dioxide (12, 14, 16, 22, and 9), in 2010 till 2014, respectively. The variety of HARD attributed to PM had been (2054, 2277, 2675, 2042, and 1895); O3 (27, 35, 58, 73 and 63); NO2 (23, 24, 15, 25, and 18); and SO2 (23, 24, 25, 30, and 20), throughout 2010-2014, respectively.
Table 1 exhibits the developments of stage nitrogen dioxide, sulfide dioxide, ozone, and particle matter and the well being endpoint of publicity to standards air pollution in ambient air of on a populated in Ahvaz metropolis, Iran.
Also, the outcome specified that the imply focus of air pollution was larger than WHO pointers customary. As may be seen in Figure 2, circumstances of cardiovascular mortality, hospital admission respiratory illness, and hospital admission heart problems associated to PM10, SO2, NO2, and O3 within the interval of the examine had an rising after which a reducing development.
Yao et al. (36) undertook a China analysis of well being burden associated to publicity to air pollution. They reported that publicity to air pollution trigger cardiovascular and respiratory illness in 7.8 million individuals (36). They reported that the untimely mortality, contributions of PM2.5, PM10, NO2, SO2, O3, and CO were11.1, 5.2, 28.9, 9.6, 23.0, and 22.2%, respectively (36).
In 2013, Jeong undertook a examine of Suwon, Korea, which examined the well being results of air air pollution on individuals. The examine noticed that the annual PM10 common was equal to 52 μg/m3. The outcomes of the examine recommend that the summer time season with a focus of two,563 μg/m3 was the best quantity of PM10 μg/m3 (37).
In Egypt Shakour et al. reported that for each 10 μg/m3 in PM10 focus, there could be a 4.1% improve in hospital admission heart problems (HARD) (38), which is decrease in comparison with different research. A 2013 examine by Habeebullah et al. (39) in Makkah, Saudi Arabia discovered that the annual common and most PM10 had been 195.5 and 782.1 μg/m3, which had been decrease than the degrees of PM10 in our examine. Particle concentrations within the current examine additionally had the best concentrations in summer time, which is the primary purpose this improve may very well be as a result of prevalence of mud storms within the Middle East areas due to wind pace and better temperature.
DeFlorio-Barker et al. (40) estimated the air air pollution ranges and inhabitants affect interplay of publicity to air air pollution. They confirmed that train intensifies the ailing results of air air pollution for these with power circumstances (40).
Kumarathasan et al. (41) within the neighborhood of a metal mill evaluation of wholesome people between cardiovascular and inflammatory mechanisms and publicity to air air pollution in wholesome people. The outcomes confirmed that the imply CO, SO2 and ultrafine particle (UFP) ranges on the day of organic sampling had been larger on the Bayview website in comparison with the College website (41). They reported that the metal mill website can affect inflammatory and vascular mechanisms (41).
In research carried out by Yarahmadi et al. (42) in Tehran on mortality associated to publicity to effective particles, the outcomes confirmed that mortality was associated to a corresponding discount in PM concentrations. The annual imply circumstances of power obstructive pulmonary illness and lung most cancers deaths associated to publicity to PM2.5 had been 158 and 142, respectively (42).
The outcomes of this examine confirmed that the extent of pollution in Ahvaz was an incredible deal larger in comparison with requirements outlined in heavy industries corresponding to oil, gasoline, petrochemical, and metal. The causes for this would possibly embrace mud storms, a lower in rainfall, and a rise in drought.
Biggeri et al. (43) studied the connection between the well being results attributed to long-term publicity to sulfur dioxide and well being endpoint on residents in Italy. This examine reported a big relationship between well being results and SO2 (43). The results of this examine confirmed that a rise of 10 μg/m3 in sulfur dioxide was related to a rise of two.4% in hospital admissions (43).
High emissions of excessive sulfur from heavy industries may very well be associated to the excessive proportion of hospital admissions for respiratory and heart problems in Ahvaz.
Bell et al. (44) within the U.S undertook comparable work, in 2004, they studied the connection between well being results and ground-level ozone. Results confirmed {that a} excessive stage of ground-level ozone elevated the chance of each day deaths, hospital admissions, and respiratory and cardiovascular ailments (10-ppb improve within the focus of ground-level ozone was attributed to a 0.52% improve in each day deaths) (44). The most vital causes that may be talked about for the distinction between the outcomes of this examine and different research is the existence of climatic traits, geography and meteorological modifications within the metropolis of Ahvaz.
Samoli et al. (45) performed a examine in 30 European cities, outlining that there was a relation between NO2 ranges and cardiovascular and respiratory mortality. According to their outcomes, a big affiliation was discovered between cardiovascular and respiratory mortality and the extent of nitrogen dioxide (45). They point out that cities with a bigger proportion of aged individuals within the inhabitants had been noticed to have the next variety of respiratory mortality (45).
In 2016, Dijkema et al. (46) studied the relation between cardiopulmonary hospital admissions and variation in concentrations of nitrogen dioxide. They discovered that there’s a larger danger of cardiopulmonary hospital admissions in areas with the next focus of nitrogen dioxide (46). Findings confirmed that constructive associations had been discovered between the degrees of nitrogen dioxide and hospital admission charges for bronchial asthma, power obstructive pulmonary illness (COPD), all cardiovascular causes, ischemic coronary heart illness, and for the second to fourth quartile relative to the primary quartile of publicity had been 1.87 (1.46–2.40), 2.34 (1.83–3.01), and a couple of.81 (2.16–3.65) for bronchial asthma; 1.44 (1.19–1.74), 1.50 (1.24–1.82), and 1.60 (1.31–1.96) for COPD) (46).
The metropolis of Ahvaz has additionally been considerably affected by fast inhabitants development, heavy trade, lack of correct transportation, and mud storms. Since air is the primary issue within the lifetime of people, respiration massive quantities of pollution can pose well being dangers to the individuals within the area. Activities associated to the event of oil and gasoline fields and petrochemical and metal undertaking industries and pipelines have elevated the focus of different pollution. Therefore, steady monitoring of the air pollutant content material in indoor and outside air high quality is a precedence. The development of yearly focus of air pollution was reducing and confirmed that the motion taken to scale back the emission of those contaminants by corrective actions corresponding to bettering the standard of gasoline in autos, rising the planting of timber, bettering the standard of companies offered within the public transport sector, lowering the manufacturing and emission by industries are efficient.
Limitations and Strengths
The essential limitations of this examine had been a scarcity of epidemiological research and calculations of relative danger (RR) and baseline incidence (BI) attributed to cardiovascular mortality, hospital admission respiratory and heart problems in people on account of standards air pollution within the examine space. To resolve this drawback, it’s essential to conduct cohort research for a number of years to calculate RR and BI. In current years, a examine of the Hoveyzeh cohort has began within the southwest of Iran. It is hoped that in a number of years, vital indicators corresponding to baseline incidence and relative danger on this area will likely be calculated and this drawback will likely be solved in future research.
The most vital strengths of the examine had been the investigation of the well being endpoint of publicity to standards air pollution in ambient air for this space (Ahvaz City, Iran). Estimating the dangers of air pollution on human well being can play an vital function in elevating public consciousness. They may also assist well being policymakers by offering a sensible information for coverage. In future research, examination of time collection evaluation will likely be performed with the assistance of statistics specialists.
Conclusion
We evaluated the implications of publicity to particle matter (PM10), floor stage of ozone (O3), sulfide dioxide (SO2), and nitrogen dioxide (NO2) within the ambient air of a populated space in Ahvaz City, Iran. Considering that Ahvaz is among the largest cities in Iran and the area from the side of urbanization, trade, and inhabitants, these findings may very well be helpful for decision-makers in different components of the nation and the world, particularly within the Middle East. According to the findings, there’s a important relationship between cardiovascular mortality (CM), hospital admissions heart problems (HACD), hospital admission respiratory illness (HARD), and elevated publicity to air pollution.
The outcomes of this examine confirmed that the focus of PM10, O3, SO2, and NO2 was larger than the WHO guideline worth. The essential brokers of circumstances well being results of publicity to PM10 had been due to the excessive stage of this pollutant. Paying consideration to reducing emissions and ranges of particle matter, the bottom stage of ozone, sulfide dioxide, and nitrogen dioxide for the discount of circumstances of CM, HACD, and HARD attributed to particle matter, nitrogen dioxide, sulfide dioxide, and ozone b are vital.
Observing trendy city planning patterns in city growth, creating public transportation (particularly metro), rising inexperienced house per capita by planting timber and creating parks in several areas of town, finishing up efficient actions in desertification, automobile alternative (worn and outdated), creating inexperienced belts round cities, lowering emissions as a result of actions of heavy industries (oil and gasoline), bettering manufacturing processes in vital industries (metal, refineries, and cement), the institution of monitoring and measuring stations, cautious monitoring and rising the final literacy of society are an important management actions that can cut back the focus of pollution and dangerous results of inhaling these substances.
Data Availability Statement
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflict of Interest
Publisher’s Note
References
1. Goudarzi G, Alavi N, Geravandi S, Idani E, Behrooz HRA, Babaei AA, et al. Health danger evaluation on human uncovered to heavy metals within the ambient air PM 10 in Ahvaz, southwest Iran. Int J Biometeorol. (2018) 62:1075–83. doi: 10.1007/s00484-018-1510-x
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
2. Morovati P, Valipour A, Geravandi S, Karimyan A, Behrooz HRA, Mohammadi MJ. Association of air high quality index associated to standards air pollution in Abadan, Iran. Fresenius Environmental Bulletin. (2018) 27:4023–8. Available on-line at: http://eprints.asaums.ac.ir/id/eprint/57
Google Scholar
3. Momtazan M, Geravandi S, Rastegarimehr B, Valipour A, Ranjbarzadeh A, Yari AR, et al. An investigation of particulate matter and related cardiovascular dangers in abadan and khorramshahr in 2014–2016. Toxin Rev. (2018) 1–8. doi: 10.1080/15569543.2018.1463266
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
4. Dobaradaran S, Geravandi S, Goudarzi G, Idani E, Salmanzadeh S, Soltani F, et al. Determination of cardiovascular and respiratory ailments brought on by PM10 Exposure in Bushehr, 2013. J Mazandaran Univ Med Sci. (2016) 26:42–52. Available on-line at: http://jmums.mazums.ac.ir/article-1-8154-en.html
Google Scholar
5. Geravandi S, Sicard P, Khaniabadi YO, De Marco A, Ghomeishi A, Goudarzi G, et al. A comparative examine of hospital admissions for respiratory ailments throughout regular and dusty days in Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res. (2017) 24:18152–9. doi: 10.1007/s11356-017-9270-4
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
6. Hashemzadeh B, Idani E, Goudarzi G, Ankali KA, Sakhvidi MJZ, Babaei AA, et al. Effects of PM 2.5 and NO 2 on the 8-isoprostane and lung perform indices of FVC and FEV 1 in college students of Ahvaz metropolis, Iran. Saudi J Biol Sci. (2019) 26:473–80. doi: 10.1016/j.sjbs.2016.11.008
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
7. Mirhoseini SH, Nikaeen M, Hatamzadeh M, Hassanzadeh A. Assessment of bioaerosol focus within the indoor environments. Health Syst Res. (2014) 10:376–85.
Google Scholar
8. Massoudinejad MR, Ghajari A, Hezarkhani N, Aliyari A. Survey of fungi bioaerosols in icu ward of taleghani hospital in tehran by petri-dish trapping approach and bioaerosol sampler in 2013. Safety Promot Inj Prev. (2015) 3:147–54. doi: 10.22037/meipm.v3i3.8800
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
9. Hay S, GRF Collaborators. Global, regional, and nationwide comparative danger evaluation of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic dangers or clusters of dangers, 1990–2016: a scientific evaluation for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2016. Lancet. (2017) 390:1345–422. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32366-8
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
10. Prüss-Üstün A, Wolf J, Corvalán C, Bos R, Neira M. Preventing Disease Through Healthy Environments: A Global Assessment of the Burden of Disease From Environmental Risks: World Health Organization (2016).
Google Scholar
13. Bhatia L. Impact of bioaerosols on indoor air quality-a rising concern. Adv Biores. (2011) 2:120–3.
Google Scholar
15. Taylor M, Retalis A, Flocas HA. Particulate matter estimation from photochemistry: a modelling strategy utilizing neural networks and synoptic clustering. Aerosol Air Qual Res. (2016) 16:2067–84. doi: 10.4209/aaqr.2015.07.0481
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
16. Lin C-C, Tsai J-H, Huang Okay-L, Yeh CK-J, Chen H-L, Chen S-J, et al. Characteristics of respirable particulate metals emitted by a beehive firework show in yanshuei space of southern Taiwan. Aerosol Air Qual Res. (2016) 16:2227–36. doi: 10.4209/aaqr.2016.08.0346
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
17. Dehdashti A, Sahranavard N, Rostami R, Barkhordari A, Banayi Z. Survey of bioaerosols sort and focus within the ambient air of hospitals in Damghan, Iran. Occup Med Quart J. (2013) 4:41–51.
Google Scholar
20. Hassani GBA, Takdastan A, Shirmardi M, Yousefian F, Mohammadi MJ. Occurrence and destiny of 17β-estradiol in water assets and wastewater in Ahvaz, Iran. Glob NEST J. (2016) 18:855–66. doi: 10.30955/gnj.002053
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
21. Tahery N, Geravandi S, Goudarzi G, Shahriyari HA, Jalali S, Mohammadi MJ. Estimation of PM 10 pollutant and its impact on whole mortality (TM), hospitalizations on account of cardiovascular ailments (HACD), and respiratory illness (HARD) consequence. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. (2021) 28:22123–30. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-12052-9
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
22. Khaefi M, Geravandi S, Hassani G, Yari AR, Soltani F, Dobaradaran S, et al. Association of particulate matter impression on prevalence of power obstructive pulmonary illness in Ahvaz, southwest Iran throughout 2009–2013. Aerosol Air Qual Res. (2017) 17:230–7. doi: 10.4209/aaqr.2015.11.0628
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
23. Goudarzi G, Geravandi S, Foruozandeh H, Babaei AA, Alavi N, Niri MV, et al. Cardiovascular and respiratory mortality attributed to ground-level ozone in Ahvaz, Iran. Environ Monit Assess. (2015) 187:487. doi: 10.1007/s10661-015-4674-4
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
24. Khaefi M, Goudarzi G, Yari AR, Geravandi S, Dobaradaran S, Idani E, et al. An affiliation between ambient pollution and hospital admitted respiratory circumstances in Ahvaz, Iran. Fresenius Environ Bull. (2016) 25:3955–61.
Google Scholar
25. Goudarzi G, Geravandi S, Idani E, Hosseini SA, Baneshi MM, Yari AR, et al. An analysis of hospital admission respiratory illness attributed to sulfur dioxide ambient focus in Ahvaz from 2011 by 2013. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. (2016) 23:22001–7. doi: 10.1007/s11356-016-7447-x
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
26. Effatpanah M, Effatpanah H, Jalali S, Parseh I, Goudarzi G, Barzegar G, et al. Hospital admission of publicity to air air pollution in Ahvaz megacity throughout 2010–2013. Clin Epidemiol Glob Health. (2020) 8:550–6. doi: 10.1016/j.cegh.2019.12.001
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
27. Yari AR, Goudarzi G, Geravandi S, Dobaradaran S, Yousefi F, Idani E, et al. Study of ground-level ozone and its well being danger evaluation in residents in Ahvaz City, Iran throughout 2013. Toxin Rev. (2016) 35:201–6. doi: 10.1080/15569543.2016.1225769
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
28. Khaniabadi YO, Polosa R, Chuturkova RZ, Daryanoosh M, Goudarzi G, Borgini A, et al. Human well being danger evaluation on account of ambient PM10 and SO2 by an air high quality modeling approach. Process Saf Environ Protect. (2017) 111:346–54. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2017.07.018
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
29. Fattore E, Paiano V, Borgini A, Tittarelli A, Bertoldi M, Crosignani P, et al. Human well being danger in relation to air high quality in two municipalities in an industrialized space of Northern Italy. Environ Res. (2011) 111:1321–7. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2011.06.012
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
30. Faridi S, Shamsipour M, Krzyzanowski M, Künzli N, Amini H, Azimi F, et al. Long-term developments and well being impression of PM2. 5 and O3 in Tehran, Iran, 2006–2015. Environ Int. (2018) 114:37-49. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2018.02.026
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
31. Karimi A, Shirmardi M, Hadei M, Birgani YT, Neisi A, Takdastan A, et al. Concentrations and well being results of short-and long-term publicity to PM2. 5, NO2, and O3 in ambient air of Ahvaz metropolis, Iran (2014–2017). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. (2019) 180:542-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.05.026
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
33. Treede R-D, Rief W, Barke A, Aziz Q, Bennett MI, Benoliel R, et al. Chronic ache as a symptom or a illness: the IASP classification of power ache for the worldwide classification of ailments (ICD-11). Pain. (2019) 160:19–27. doi: 10.1097/j.ache.0000000000001384
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
34. Chung Okay-F, Yeung W-F, Ho FY-Y, Yung Okay-P, Yu Y-M, Kwok C-W. Cross-cultural and comparative epidemiology of insomnia: the Diagnostic and statistical handbook (DSM), International classification of ailments (ICD) and International classification of sleep issues (ICSD). Sleep Med. (2015) 16:477–82. doi: 10.1016/j.sleep.2014.10.018
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
35. Organization WH. ICD-10: International Statistical Classification Of Diseases And Health-Related Problems. Geneva: WHO (2010). p. 64–7.
Google Scholar
36. Yao M, Wu G, Zhao X, Zhang J. Estimating well being burden and financial loss attributable to short-term publicity to a number of air pollution in China. Environ Res. (2020) 183:109184. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2020.109184
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
37. Jeong S. The impression of air air pollution on human well being in suwon metropolis. Asian J Atmos Environ. (2013) 7:227–33. doi: 10.5572/ajae.2013.7.4.227
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
39. Habeebullah T. Health impacts of PM10 utilizing AirQ2.2.3 mannequin in Makkah. J Basic Appl Sci. (2013) 9:259–68. doi: 10.6000/1927-5129.2013.09.34
CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
40. DeFlorio-Barker S, Lobdelle DT, Stone SL, Boehmer T, Rappazzo KM. Acute results of short-term publicity to air air pollution whereas being bodily lively, the potential for modification: a overview of the literature. Prev Med. (2020) 106195. doi: 10.1016/j.ypmed.2020.106195
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
41. Kumarathasan P, Vincent R, Blais E, Bielecki A, Guénette J, Filiatreault A, et al. Cardiovascular and inflammatory mechanisms in wholesome people uncovered to air air pollution within the neighborhood of a metal mill. Part Fibre Toxicol. (2018) 15:1–17. doi: 10.1186/s12989-018-0270-4
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
42. Yarahmadi M, Hadei M, Nazari SSH, Conti GO, Alipour MR, Ferrante M, et al. Mortality evaluation attributed to long-term publicity to effective particles in ambient air of the megacity of Tehran, Iran. Environ Sci Pollut Res. (2018) 25:14254–62. doi: 10.1007/s11356-018-1680-4
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
43. Biggeri A, Bellini P, Terracini B, Italian MG. [Meta-analysis of the Italian studies on short-term effects of air pollution]. Epidemiol Prev. (2001) 25:1–71.
Google Scholar
44. Bell ML, McDermott A, Zeger SL, Samet JM, Dominici F. Ozone and short-term mortality in 95 US city communities, 1987-2000. JAMA. (2004) 292:2372–8. doi: 10.1001/jama.292.19.2372
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
45. Samoli E, Aga E, Touloumi G, Nisiotis Okay, Forsberg B, Lefranc A, et al. Short-term results of nitrogen dioxide on mortality: an evaluation throughout the APHEA undertaking. Eur Resp J. (2006) 27:1129–38. doi: 10.1183/09031936.06.00143905
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar
46. Dijkema MB, van Strien RT, van der Zee SC, Mallant SF, Fischer P, Hoek G, et al. Spatial variation in nitrogen dioxide concentrations and cardiopulmonary hospital admissions. Environ Res. (2016) 151:721–7. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2016.09.008
PubMed Abstract | CrossRef Full Text | Google Scholar

