For Japan, the combination of AI in varied fields represents a promising mixture of innovation and prudence. The vital scarcity of cybersecurity professionals in Japan highlights an pressing and strategic response to this rising hole.
Organizations and governments world wide, together with Japan, face the twin problem of mitigating threat and embracing speedy advances in AI. This contains managing uncertainty whereas accelerating innovation and adoption to reap the advantages of this transformative expertise.
Japan’s distinctive place in AI
Japan is understood for its cautious method to threat, however additionally it is recognized for its modern contributions to expertise, notably in good robotics and automotive AI. However, the report says Japan’s superior capabilities in AI-enabled {hardware} usually are not equally matched by its software program capabilities, and Japan depends on large-scale overseas language fashions for generative AI.
Japan faces distinctive hurdles to the event and adoption of AI, together with restricted information availability and cultural attitudes towards enterprise threat. These components complicate the combination of AI applied sciences inside conventional enterprise frameworks.
A latest examine by Barracuda, “Japan’s Small Business Cyber Resilience: Overcoming Doubts concerning the Future of AI,” examines the affect of AI on Japan’s small and medium-sized companies (SMBs). This reveals a mixture of optimism about the advantages of AI and considerations about safety, data and expertise gaps.
The survey highlighted a normal sense of optimism amongst small organizations in Japan concerning the constructive affect AI can have on enterprise operations. The majority of those corporations count on the implementation of AI options to result in fewer workers over the subsequent two years, with 66% anticipating fewer full-time workers and 70% hiring fewer freelancers and contractors. We count on this to cut back our reliance on While this pattern is anticipated to result in decrease prices and decreased demand for human sources for companies, it additionally highlights the unsure way forward for employees in roles inclined to automation.
In addition to lowering prices, corporations count on AI to enhance operational effectivity throughout quite a lot of features comparable to advertising and marketing and buyer care. About 67% predict that quickly greater than half of their content material will likely be generated by AI instruments, and 60% imagine that AI will grow to be the first interplay level with prospects. Additionally, 76% count on quicker and extra correct buyer insights due to AI.
Strengthening cybersecurity with AI
More broadly, 65% of respondents imagine that AI instruments will streamline their cybersecurity wants and cut back reliance on human safety groups and third-party providers. With a extreme scarcity of cybersecurity specialists in Japan, integrating AI for automated menace detection and response is taken into account important to strengthen the safety of companies of all sizes. Masu.
Most organizations acknowledge the necessity for exterior help to maximise using AI for enterprise advantages. The majority of corporations surveyed (76%) indicated that they want a companion to analysis and discover AI. The identical share (77%) need assist implementing AI options and the continuing administration of those applied sciences. Japanese safety distributors and managed service suppliers are well-positioned to assist small and medium-sized enterprises harness the advantages of AI.
ChatGPT, launched by OpenAI in November 2022, showcased the facility of generative AI instruments to create pure and fascinating interactions. Despite the widespread consideration, corporations are taking a cautious stance towards generative AI. Awareness doesn’t imply complete understanding. While 56% perceive the distinction between generative AI and different forms of AI, comparable to machine studying, 44% admit to having restricted or no understanding. As a consequence, many Japanese corporations have positioned limits on using AI because of the potential dangers.
Approximately 69% of corporations are conscious of the dangers related to utilizing generative AI within the office. 18% permit its use, 6% use it extensively, 12% use it in restricted group environments, and 62% don’t formally permit its use, probably rising safety dangers. It suggests using sexual secrets and techniques. Concerns additionally embody information safety (57% of respondents), lack of regulatory framework (47%), and opaque AI decision-making processes (31%). Furthermore, 13% are involved that their AI methods will likely be compromised by cyber attackers.
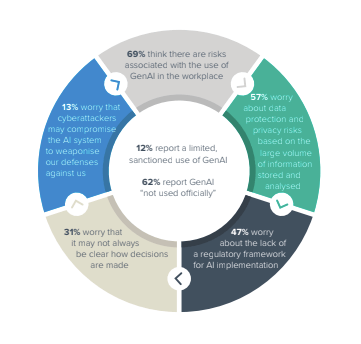
Risks of utilizing generative AI (Source – Barracuda)
Evolution of AI and cyber threats
There is critical uncertainty concerning the function of AI in evolving cyber threats. Approximately 55% of companies are not sure how AI will likely be utilized in e mail assaults, and comparable uncertainty exists for denial of service (62%), malware (57%), API assaults (56%), and cyber assaults. It additionally extends to espionage (55%). ).
Despite these uncertainties, e mail threats stay a serious concern for Japanese small and medium-sized companies, with 53% citing account takeover assaults as their prime menace. This type of identification theft can permit attackers to misuse your account, resulting in phishing scams, information theft, and extra. Other vital threats embody phishing and social engineering (37%), and ransomware can also be vital (39% reported ransomware as their prime concern, primarily by way of e mail) .
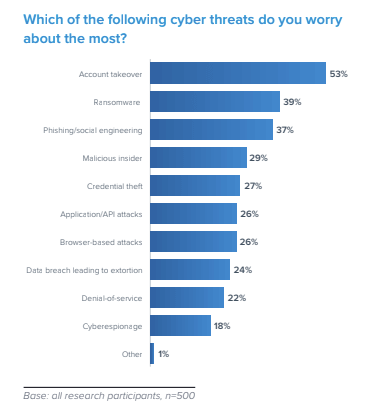
Cyber threats for Japanese companies (Source – Barracuda)
Survey members usually perceive the function of AI in strengthening cyber defenses, notably in areas comparable to e mail safety and worker cybersecurity coaching. However, there’s ambiguity concerning the effectiveness of AI in different areas, maybe as a result of these areas are much less acquainted to small companies.
When requested which AI-enhanced safety measures would make their group safer, 36% cited AI-enhanced e mail safety, particularly in opposition to superior threats like deepfakes. An additional 24% imagine AI can assist extra custom-made and frequent coaching packages. The advantages of AI in steady menace intelligence and response carried out by safety operations facilities (SOCs) have been much less clearly understood.
This analysis reveals deficiencies in AI-specific practices and insurance policies required for accountable use of AI. Although 52% of corporations conduct worker coaching on AI use and vulnerabilities, solely 35% of corporations have a proper coverage governing using AI. Even fewer corporations have complete governance buildings in place, comparable to authorized frameworks. This signifies a scarcity of management and administration over AI purposes inside the enterprise.
According to the newest ICS2 Cybersecurity Workforce Survey, Japan has almost 500,000 cybersecurity professionals, a big year-over-year improve of 23.8% in comparison with the worldwide common of 8.7%. Despite this development, demand far exceeds provide, with a scarcity of 110,254 professionals, a rise of 97.6% year-on-year and considerably larger than the worldwide common of 12.6%. exceeds. This hole is unprecedented in comparison with different nations assessed within the ICS2 examine.
This macro perspective displays the each day challenges of small and medium-sized companies, particularly in relation to AI-driven cyber threats.
Makoto Suzuki, Barracuda’s Japan regional gross sales director, highlighted the findings. Japanese SMEs acknowledge the advantages of AI in bettering enterprise productiveness, however stay cautious of the cyber threats it poses. Suzuki stated, “This will allow corporations to take full benefit of AI’s potential to revolutionize enterprise efficiency and competitiveness by optimizing processes, lowering prices, bettering high quality, and delivering new insights and concepts. It could also be hindered.”
Muhammad Zurhusni
As a expertise journalist, Zul focuses on subjects comparable to cloud computing, cybersecurity, and disruptive applied sciences for the enterprise trade. In addition to his expertise background, he has experience in internet hosting webinars and presenting content material on video.

