Soil properties
Figure 4 reveals that D. damavandica is prone to develop in quite a lot of soil varieties, however the majority of soil varieties in its habitat are heavy clay soils, particularly clay loams, which offer ion-accumulating properties.
Figure 4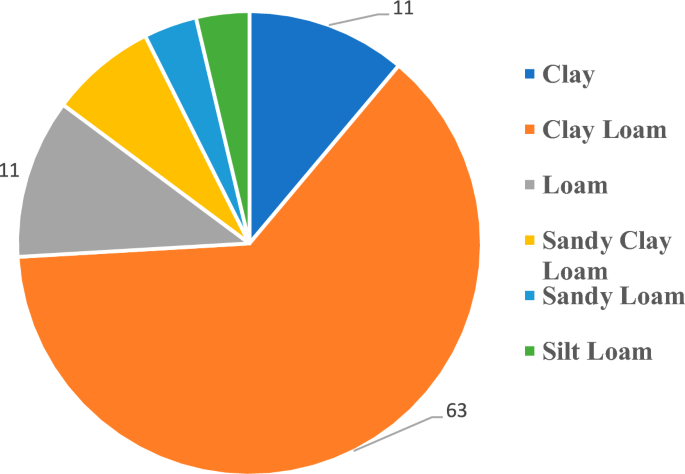
Percentage and sort of soil high quality of soil samples collected from D. damavandica habitats.
Subsequently, the imply soil particle sizes of the D. damavandica habitat and the management space have been in contrast utilizing Student’s t-test, which demonstrated vital variations in silt parameters (Table 1).With regard to pH, some researchers have discovered pH values of seven.6-7.85 within the deserted roofs of the Ubaji gold mine and the Ilam bitumen mine, that are much like the outcomes of this study13,39.
Table 1. Student’s t take a look at comparability of soil parameters in habitats and controls.
Furthermore, bearing in mind the presence of Mt. Damavand, volcanic soils40,41 and the presence of heavy metals in such conditions42, we investigated the whole focus of HMs within the related soils of D. damavandica after which in contrast them with management areas inside and outdoors the habitat. The investigation of the floor soil contamination (0-20 cm) across the roots of D. damavandica and the management space (no crops current) is proven in Figures 5, 6 and seven. It must be famous that the border (black dot) between the management pattern (0) and the habitat (1) is proven within the following determine. In the path from the arrow in the direction of the precise aspect of the horizontal axis, the frequency of crops will increase. On the opposite hand, within the path from the arrow in the direction of the left aspect, the management space approaches the habitat.
Figure 5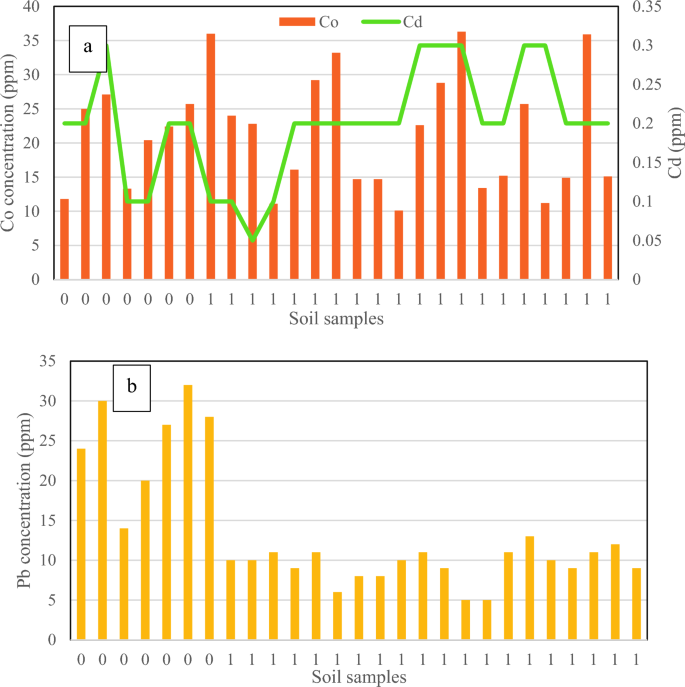
Results for (a) cadmium and cobalt, and (b) lead in D. damavandica habitats and management plots are proven on the horizontal axis as “0 and 1,” respectively.
Figure 6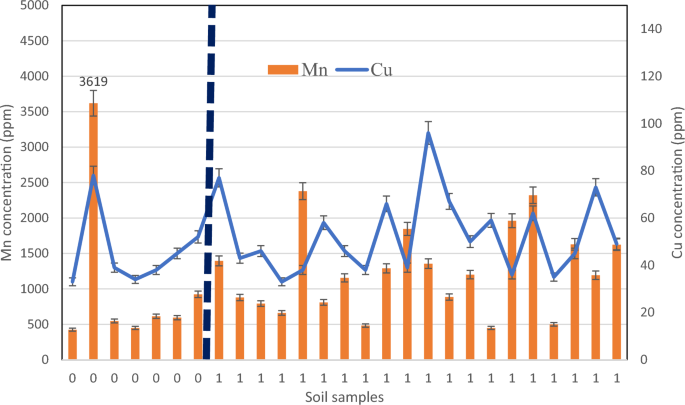
Manganese and copper survey leads to D. damavandica habitats and management websites.
Figure 7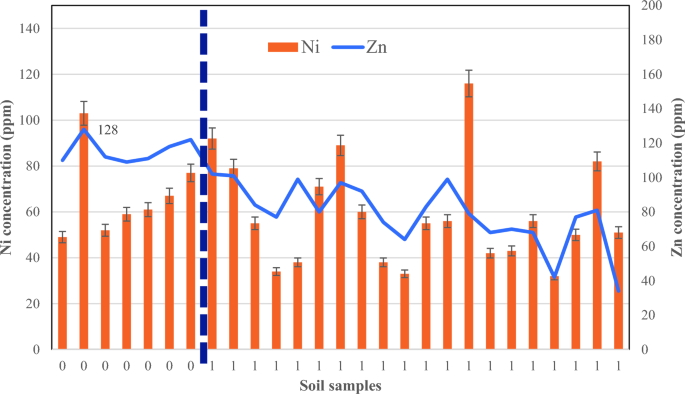
Results for nickel and zinc in D. damavandica habitats and management areas.
The outcomes of cobalt and cadmium in Figure 5 confirmed no explicit tendencies between the habitat and the management space. The most and minimal complete concentrations of cobalt within the management space have been equal to 27 and 13 (ppm), respectively, whereas within the habitat, the utmost and minimal concentrations of cobalt have been 36 and 10 (ppm), respectively, indicating the suitability of the crops. The most and minimal complete concentrations of cadmium in each areas have been discovered to be equal to lower than 0.5 (ppm), respectively.
As for lead, a major lowering pattern was noticed within the presence of D. damavandica, as proven in Figure 6 and Table 2. The highest and lowest complete lead concentrations in soils with D. damavandica have been 28 and 1, respectively. Thus, the whole lead focus was diminished by 60%.
Table 2 HMs information evaluation and comparability of imply information utilizing Student’s t take a look at.
The outcomes of complete manganese and copper concentrations didn’t present any explicit tendencies within the management and habitats (Fig. 6). However, the outcomes point out that native crops have the power to coexist with manganese and copper concentrations.
The nickel outcomes confirmed no explicit tendencies between the habitat and management websites (Fig. 7). The imply complete nickel concentrations within the management and habitat websites have been equal to 66.86 ppm and 58.60 ppm, respectively.
According to Figure 7, the zinc evaluation confirmed a transparent pattern between the management space and the habitat. However, the areas farther from the habitat have larger zinc values. It must be famous that the additional away from the habitat the whole zinc focus reaches 128 ppm, whereas within the habitat the typical focus is 78.55 ppm. Thus, the native crops diminished the typical zinc focus by 40% by means of phytoremediation.
In each habitat and management, HMs concentrations have been beneath the soil contamination requirements (Table 2). However, the management revealed extra concentrations of Cu, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn in comparison with the habitat, whereas vital imply comparisons have been made for Zn and Pb. Moreover, Zn focus within the management (115 ppm) was larger than the soil customary (100 ppm). Interestingly, the presence of D. damavandica considerably diminished the concentrations of each components.
Phytoremediation effectivity index
The means of D. damavandica in phytoremediation of soil HM was calculated utilizing the typical of indices corresponding to BF, BAC, and TF as proven in Figure 8 .
Figure 8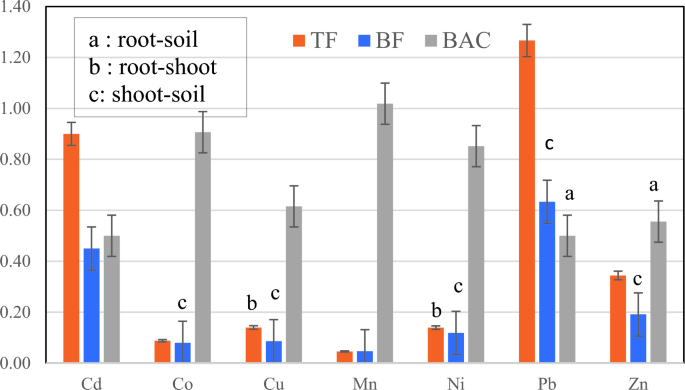
Comparison of calculated indices corresponding to TF, BF, and BAC of D. damavandica (a, b, and c symbolize the significance of the elements proven within the graph).
Overall, the BF values have been lower than 1 for all poisonous metals (Figure 8). The calculated phytoremediation index outcomes confirmed that D. damavandica had comparatively larger TF values than BF for a similar metals. The TF values for Pb higher than 1 point out phytoextraction of the plant. Previous research have additionally proven profitable removing of Pb from contaminated soils by extraction with Tamarix smyrnensis43, Armeria arenaria44, Sesbania exaltata45, and Pelargonium hortorum46. Note that sequential phytoextraction makes use of indigenous crops which have the pure means to build up excessive concentrations of HMs (hyperaccumulators). Moreover, the TF < 1 および BAC > 1 reveals the power of phytostabilization.47 Thus, within the current examine, D. damavandica has the power to phytostabilize Mn. In crops appropriate for phytoremediation, the component focus within the aboveground elements is larger than that within the soil.48,49
The outcomes confirmed that the imply values of Zn and Pb have been vital in each root and shoot soils (Fig. 8), whereas Cu, Mn, and Ni have been proven to be vital in roots and shoots.Furthermore, the comparability of shoot and soil means confirmed that Co, Cu, and Ni have been vital.
Results confirmed that, aside from Mn and Pb, different HMs in aboveground tissues have been diminished in comparison with the related soil and adopted a soil > root > shoot sample.
Interestingly, the sample for Mn is root > soil > shoot and for Pb is soil > shoot > root. Thus, the excessive quantity of Pb within the shoots of D. damavandica results in larger TF than different components. Previous research have additionally reported larger concentrations of Cd, Mo and Pb within the aerial elements of Hordeum bulbosum L., indicating its potential for phytoremediation.13 Similarly, accumulation of Pb within the dry weight of shoots and roots of Atriplex sp. has additionally been reported beforehand.50
Furthermore, Achillea willhelmsii, Stipa barbata and Aconthophyllum microcephallam have been proven to be appropriate choices for soil modification as they’d the very best HM uptake concentrations with Pb, Zn and Cd concentrations of 103.7, 237.3 and 0.9 mg/kg, respectively51.
The related soil samples and the roots and aboveground elements of D. damavandica have been then noticed underneath a subject emission scanning electron microscope (FE-SEM) outfitted with an vitality dispersive spectrometer (EDX) detector, as proven in Figure 9. The outcomes confirmed the presence of Zn and Pb ions within the roots and aboveground elements of D. damavandica. The presence of Pb and Zn within the EDX spectrum in Figure 9b confirmed the presence of Pb within the root and shoot tissues.
Figure 9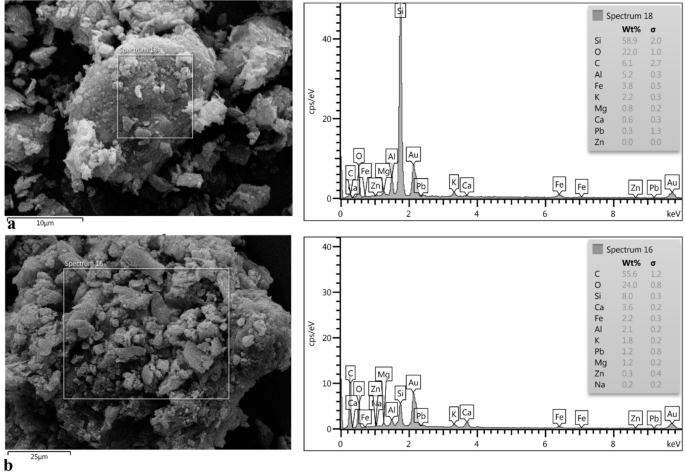
(a) Associated soil and (b) FESEM-EDX of roots and aboveground elements of D. damavandica.
Furthermore, lead accumulation has been noticed within the leaves of avenue plants52, whereas lead and zinc have been reported within the roots and aboveground elements of D. damavandica by FESEM evaluation, as proven in Figure 9. Other species corresponding to Commelinus communis, Chrysanthemum rubra, and Bayberry additionally are likely to accumulate larger concentrations of manganese within the aboveground elements than within the roots, indicating a comparatively excessive metallic transport capacity18.
It has been argued that the toxicity of HMs in crops with in depth root methods and excessive biomass leads to the very best phytoremediation effectivity in low to medium ranges,53 and the outcomes of this examine validate D. damavandica. Meanwhile, D. damavandica is practiced as a medicinal pores and skin cream and the outcomes of this examine emphasize the security of the natural drugs.

