Amidst the stunning pattern of rising colon most cancers circumstances amongst younger folks, new analysis has recognized potential sources.
Researchers on the University of California, San Diego have linked a bacterial toxin referred to as colibactin to a rise in early onset circumstances.
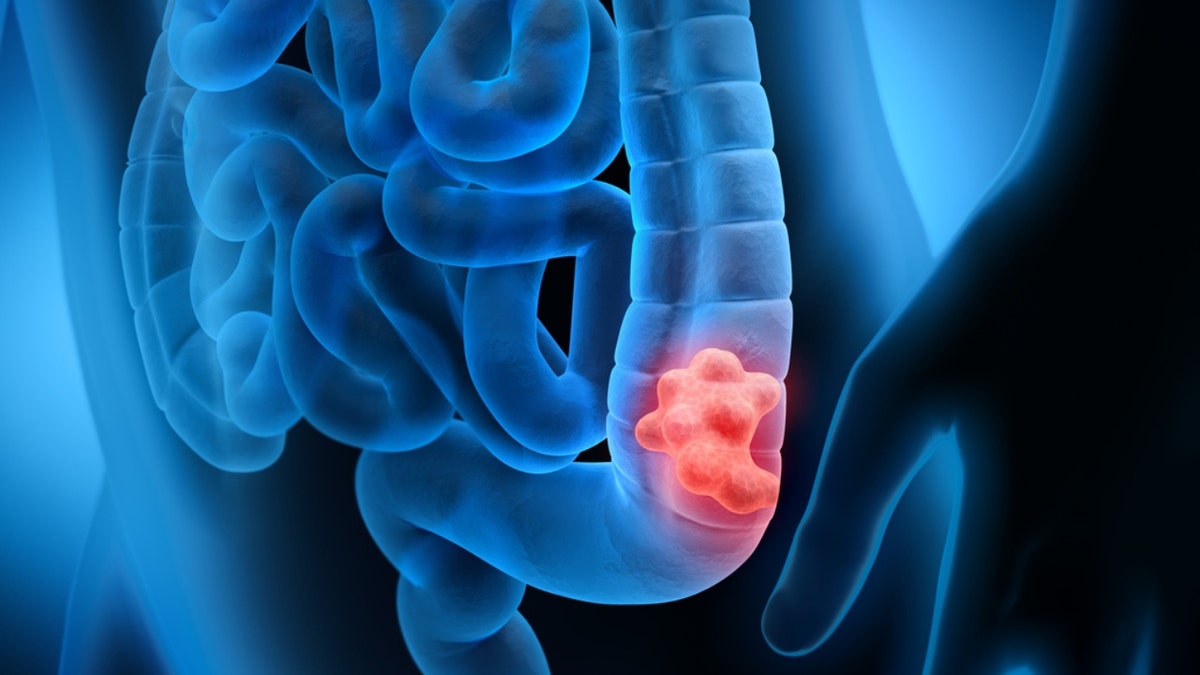
According to the researchers, colibactin is produced by sure strains of E. coli (Escherichia coli) discovered within the colon and rectum.
Research means that colorectal most cancers threat diminished by this widespread vitamin
Research has discovered that publicity to bacterial toxins in early childhood can alter colon cells’ DNA in a manner that will increase the danger of creating colorectal most cancers by the age of fifty, research have discovered.

In this examine, the researchers analyzed 981 colorectal most cancers genomes from early-onset and late-onset colorectal most cancers sufferers in 11 international locations. (istock)
The examine, funded by Cancer Research UK, was revealed within the journal Nature on April twenty third.
“They might be a long time forward of schedule to develop colorectal most cancers.”
In this examine, the researchers analyzed 981 colorectal most cancers genomes from early-onset and late-onset colorectal most cancers sufferers in 11 international locations.
Those who’ve been preexposed to colibactin have discovered that they’ve sure mutations of their DNA, that are primarily proven to happen within the first decade of their lives.
Research has discovered that publicity to bacterial toxins in early childhood can alter colon cells’ DNA in a manner that will increase the danger of creating colorectal most cancers by the age of fifty, research have discovered. (istock)
The group was 3.3 occasions extra prone to develop early-onset colorectal most cancers than these recognized after age 70.
These mutations have been discovered to account for 15% of early genetic modifications that enhance the danger of colorectal most cancers.
The girl says ChatGpt saved her life by serving to to detect most cancers. The physician missed
“We detected mutation signatures of colibactin in over 50% of colorectal tumors in sufferers below the age of 40, in comparison with lower than 10% of tumors in older adults,” stated Alexandrov.
“If somebody acquires one in every of these driver mutations by the age of 10, it might be a long time forward of the anticipated growth of colon most cancers, and it might be at age 40 as an alternative of 60,” says Alexandrov.
Researchers say that the truth that microbial publicity can go away behind a “everlasting genome imprint” within the first few years of life is the truth that it’s prone to be “surprisingly calm.”
As docs talk about the prognosis, actuality star shares a deadly melanoma replace
“From my perspective, investing in childhood prevention, wholesome residing and analysis isn’t necessary. That’s important.”
Dr. Emil Lu, a board-certified oncologist and inner drugs doctor on the University of Minnesota, agrees that the microbial flora – the “constellation of microorganisms containing micro organism that dwell below regular circumstances inside our intestine” is a possible perpetrator of early onset colorectal most cancers.
Click right here to get the Fox News app
“Of course of concern is the long-term interval between publicity to micro organism early in life and the prognosis of related most cancers.”
Potential limitations
Alexandrov famous that the examine offers “sturdy genomic proof” for a “salient affiliation” between colibactin and early-onset colorectal most cancers, however can’t show a causal relationship.
Statistics present that previously 20 years, adults below the age of fifty have doubled. (istock)
“The conclusive proof of causality includes long-term potential research starting in early childhood monitoring microbial colonization and monitoring most cancers incidence over a long time.”
Lou agreed to this limitation and famous the complexity of most cancers components.
Click right here to enroll in our well being e-newsletter
“There are many facets of the environment that may play a job within the growth of most cancers, each inside and outdoors our our bodies,” he stated. “It’s tough to say, “A single issue given (on this case, whether or not a bacterial toxin is the true or perhaps a main explanation for colon most cancers.”
“Providing proof of potential associations units the inspiration for extra in-depth analysis to find out whether or not there’s a true trigger and impact,” added Lou.
“If the present pattern continues, colorectal most cancers is predicted to be a number one explanation for cancer-related deaths in younger adults by 2030.”
Alexandrov famous that the findings don’t but assure screening or modifications to therapy tips, however highlights the “necessary function of childhood microbial publicity” by way of long-term most cancers threat.
“We are actively working to develop screening assessments to detect the long-term results of colibactin publicity, with the purpose of translating these findings into precise prevention methods within the close to future,” he added.
For well being articles, please go to www.foxnews.com/well being
Statistics present that previously 20 years, adults below the age of fifty have doubled.
“If the present pattern continues, colorectal most cancers is predicted to be the main explanation for cancer-related deaths in younger adults by 2030,” the researchers concluded.

