AI expertise can be utilized to detect doubtlessly deadly clots earlier than they assault.
It says that, in line with scientists on the University of Tokyo, they created a non-invasive technique for observing coagulation exercise within the blood when it happens.
What is Artificial Intelligence (AI)?
Too excessive platelet counts can enhance the chance of clots.
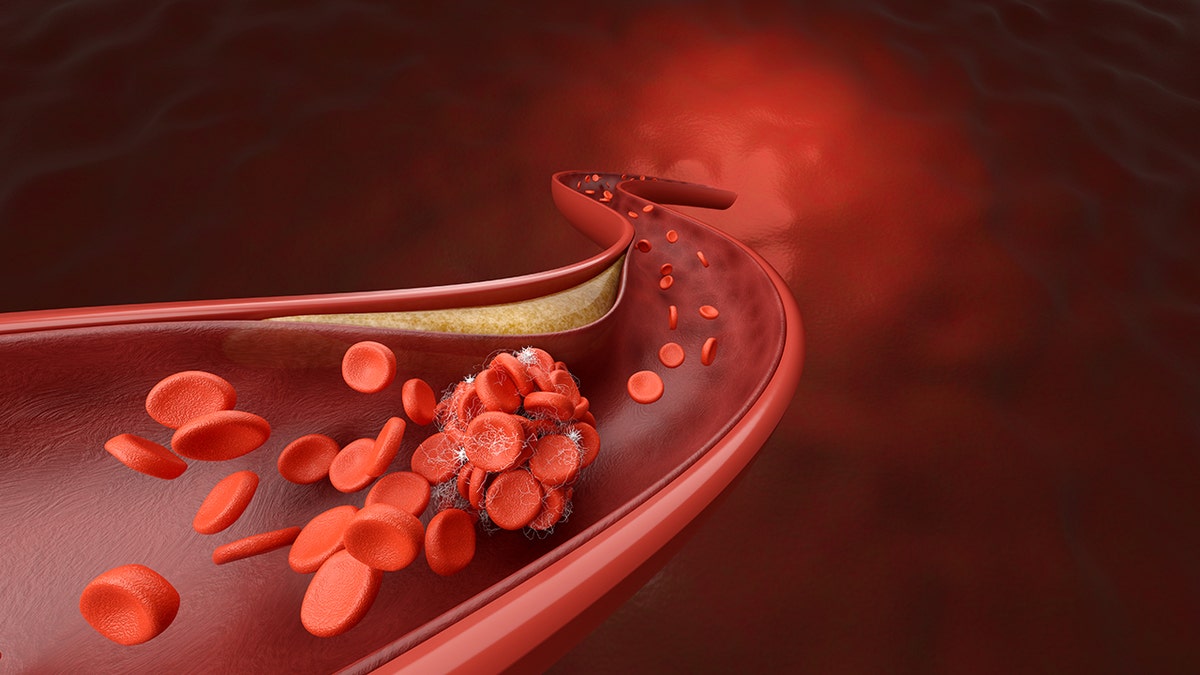
Scientists on the University of Tokyo have found a non-invasive technique for observing coagulation exercise within the blood. (istock)
To stop harmful blood clots, sufferers with coronary artery illness are normally handled with antiplatelet drugs.
How the instrument works
Traditional strategies for monitoring platelet exercise typically depend on oblique measurements or invasive procedures.
With AI instruments, high-power microscopes act like “ultra-fast cameras that take sharp photographs of circulation blood cells.”
Artificial intelligence transforms affected person care and reduces burnout, docs say
“Just as visitors cameras seize each automobile on the highway, our microscope captures hundreds of photos of blood cells transferring each second,” he stated. “Then we’ll use synthetic intelligence to research these photos.”
AI can distinguish between single platelets (“one automobile”), chunks of platelets (“like a visitors jam”), or white blood cells tagged alongside (“like a police automobile caught in a jam”).
“Now, docs typically give them blood thinning remedy and wish them to be at work. This manner we have been capable of see if the remedy was really working.”
“The method stands out as a result of docs can immediately observe platelets within the bloodstream and measure how they work together and kind plenty in actual time,” says Godaisaku, a professor within the Department of Chemistry on the University of Tokyo, on this launch.
“Our analysis has proven to be extraordinarily efficient in sufferers with coronary artery illness, the most typical reason for coronary heart assaults and one of many main causes of loss of life within the US and all over the world,” he added.
Researchers say conventional strategies of monitoring platelet exercise typically depend on oblique measurements or invasive procedures. (istock)
When researchers examined the expertise of greater than 200 sufferers, they found that folks with extra extreme coronary heart issues had extra clumps of their blood.
They famous that blood samples taken from the affected person’s arms and examined with the instrument had roughly the identical outcomes as blood taken immediately from the arteries of the center.
Impact on remedy
Harvey Castro, a Texas-based emergency doctor and AI knowledgeable, described the influence as essential for affected person care.
Click right here to get the Fox News app
“This expertise turns regular venous drawing into residing telemetry with platelet conduct, giving the reply in seconds reasonably than hours.”
Researchers say these developments might change the usual of take care of coronary coronary heart illness sufferers.
Click right here to enroll in our well being e-newsletter
“Usually, if a health care provider needs to know what is going on on within the arteries, particularly the coronary arteries, he ought to do invasive procedures, equivalent to inserting a catheter into the wrist or gro diameter to gather blood,” Hirose stated.

In a research of the effectiveness of the instrument, common blood assessments from the arm confirmed roughly the identical outcomes as blood taken immediately from the arteries of the center. (istock)
“What we discovered was that merely taking a standard blood pattern from the vein in our arm can present significant details about platelet exercise throughout the artery.”
For well being articles, please go to www.foxnews.com/well being
Goda agreed that the instrument will allow safer and extra customized remedies for coronary heart illness sufferers.
“Now, docs typically give them blood thinning remedy and hope they’re at work,” he stated. “Using this technique, we have been capable of see if the remedy was really working in every affected person.”
Potential limitations
Castro warned that the expertise will not be but prepared for widespread use.
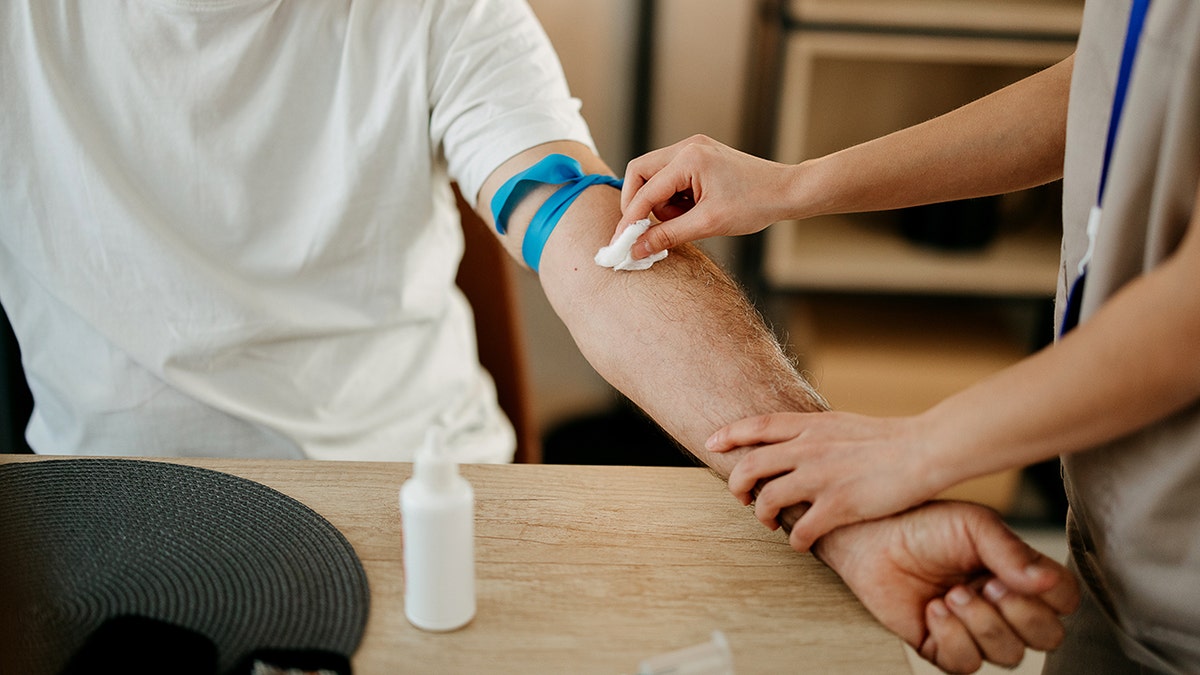
“What we discovered was that merely taking a standard blood pattern from the vein in our arm can present significant details about platelet exercise throughout the artery.” (istock)
Looking forward, after additional analysis, Castro envisions that this innovation might change affected person point-of-care selections.
“Five years from now, I can think about a point-of-care analyzer that may modify antiplatelet drugs and the way to shortly and safely titrate oxygen within the affected person in entrance of me,” he stated.

