Newou can take heed to Fox News articles!
A brand new EEG take a look at may detect early indicators of Alzheimer’s illness earlier than prognosis in simply three minutes.
This not too long ago examined a brand new method referred to as fastball EEG in sufferers’ houses, in line with researchers at Bath and Bristol University.
When an individual sees a sequence of photos, the three-minute take a look at data electrical exercise within the mind. It is designed to select up indicators of delicate cognitive impairment (MCI), which frequently precedes Alzheimer’s illness.
The threat of dementia was diminished with one basic well being intervention, the research stated
Fastball is a “passive” EEG take a look at, so it mechanically takes up mind responses with out the necessity for contributors to reply questions or recall info.
This makes it much less doubtless that they are going to be influenced by elements like nervousness, schooling, tradition and language, led by Dr. George Stottart, a cognitive neuroscientist on the University of Bath’s School of Psychology.
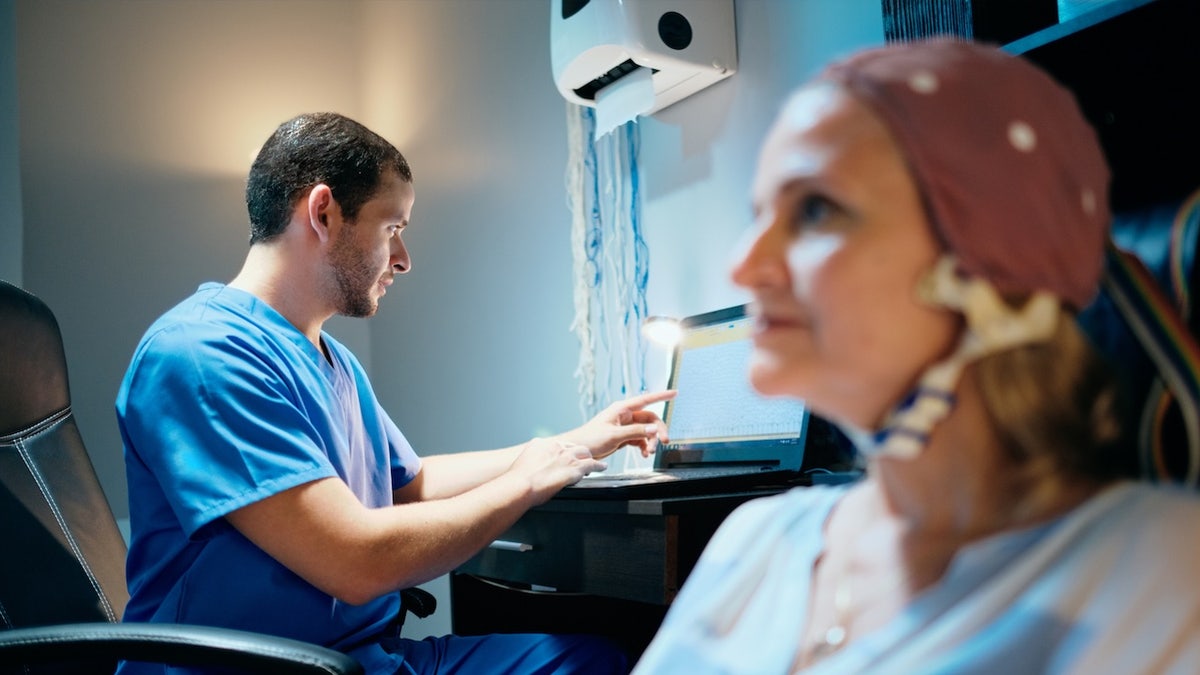
A brand new EEG take a look at may detect early indicators of Alzheimer’s illness earlier than prognosis in simply three minutes. (istock)
The trial examined 53 sufferers with delicate cognitive impairment and 54 wholesome aged individuals with 54 wholesome older adults with instruments to measure reminiscence expertise. It was then retested a 12 months later.
Omega-3 might assist shield ladies from Alzheimer’s illness, in line with a brand new research
Patients with MCI have been discovered to “considerably cut back” memory-related mind responses in comparison with sufferers with out cognitive decline.
The findings have been printed in Journal Brain Communications.
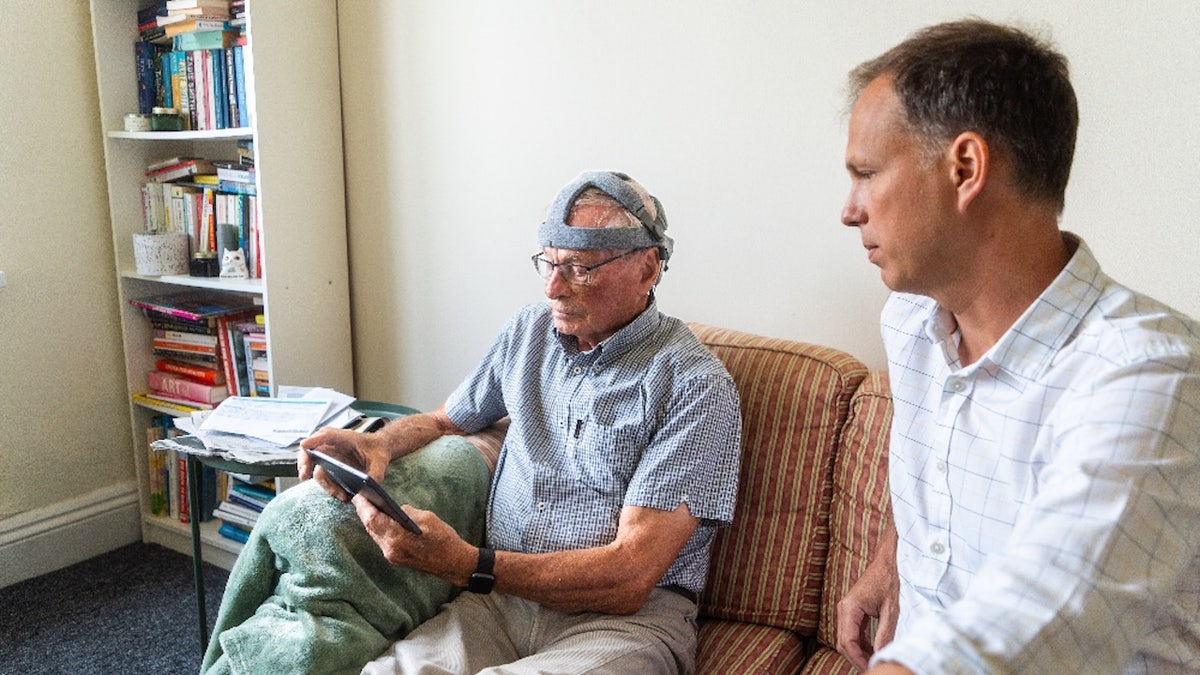

A wholesome volunteer, John Stennard is taking a fastball take a look at at residence with Dr. George Stottart of Bath University. (University of Bath)
“I used to be shocked on the reliability of retesting checks in wholesome aged individuals,” Stottart stated. “A one-year follow-up reveals that measurements stay secure and in wholesome aged individuals, fastballs produce constant outcomes over time.”
According to Stothart, the principle limitation is that researchers didn’t have biomarker information for contributors in MCI as a consequence of price and useful resource constraints.
“It could also be value investigating how this method enhances different diagnostic strategies.”
“However, ongoing medical validation research within the UK and the US, involving 1,000 sufferers every, at the moment embrace in depth biomarker compensation,” he famous.
The hope is that this device will be deployed to be used in a health care provider’s workplace, reminiscence clinic, or at residence, and can assist allow the prognosis of earlier Alzheimer’s illness.
Research reveals why “superagers” preserve “wonderful reminiscences” within the 80s
This may enable sufferers to entry main Alzheimer’s illnesses early, similar to donanemab and lecanemab, that are only at early levels of illness development, the researchers stated.
“The affected person himself has not obtained the outcomes straight from the fastball,” Stottart stated. “Instead, outcomes are supplied to clinicians, who combine them right into a broader diagnostic evaluation.”
When an individual sees a sequence of photos, the three-minute take a look at data electrical exercise within the mind. It is designed to select up indicators of delicate cognitive impairment (MCI). (istock)
“Fastballs are one other invaluable device that clinicians can select to incorporate as a part of their diagnostic battery.”
Dr. Christopher Weber, senior director of the Global Science Initiative on the Alzheimer’s Association in Chicago, stated the expertise may very well be a non-invasive device for detecting reminiscence adjustments that might signify the early levels of Alzheimer’s illness.
Click right here to get the Fox News app
“This contains confirming these findings in a bigger, extra consultant research inhabitants the place research contributors are examined to verify that there are mind adjustments related to Alzheimer’s illness.”
The hope is that this device will be deployed to be used in a health care provider’s workplace, reminiscence clinic, or at residence, and can assist allow the prognosis of earlier Alzheimer’s illness. (istock)
Weber additionally famous that the method doesn’t seem to find out the reason for reminiscence loss.
“As a consequence, it is unclear what the outcomes of this take a look at imply about your Alzheimer’s illness and your well being,” he stated. “Therefore, even when the method proves itself in additional analysis, extra checks contemplating disease-related biomarkers and mind imaging are prone to be needed to tell remedy or threat discount.”
Click right here to enroll in our well being e-newsletter
Despite the restrictions, Weber stated that fastballs might show helpful in serving to them with preliminary screening and conversations with the affected person’s physician.
“And it might be value investigating how this method can complement different diagnostic strategies, similar to PET scans, blood checks, and cognitive assessments of ‘paper and pencils,” he added.
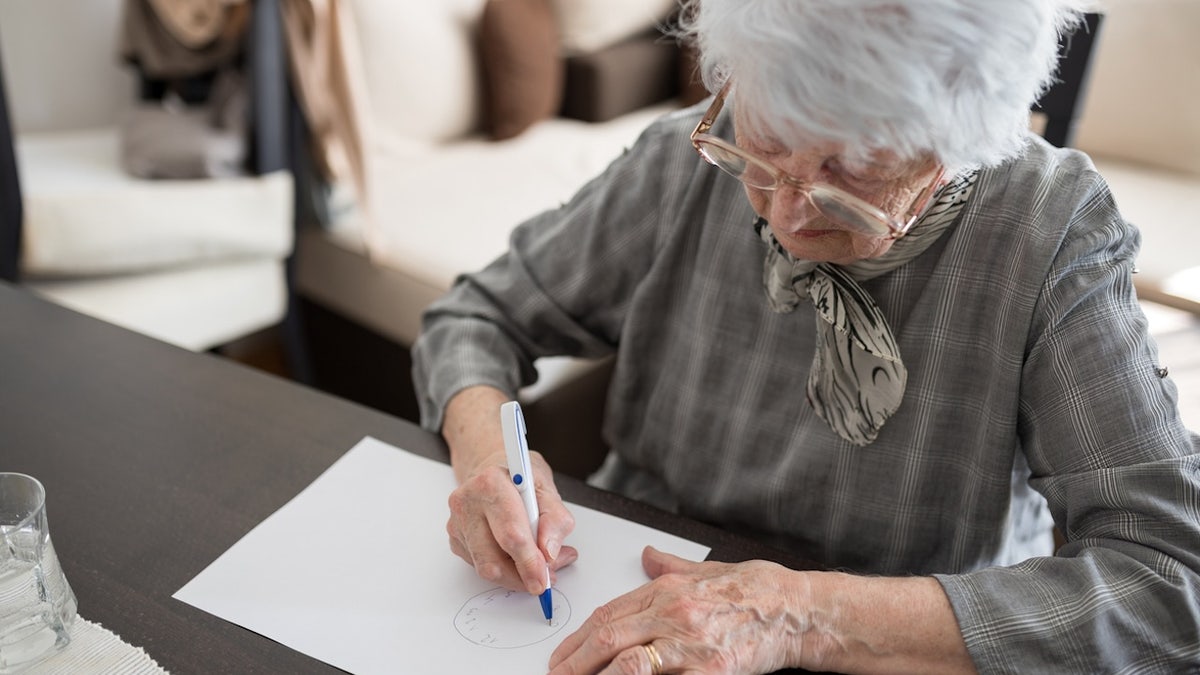

Currently, pet scans, blood checks, and “paper and pencil” cognitive scores are at the moment getting used to observe signs of Alzheimer’s illness. (istock)
Weber suggested that future use of at-home screening or testing ought to be completed in a “cautious and managed method.”
He stated, “When contemplating an Alzheimer’s or dementia-related take a look at, it is essential to have a dialog along with your healthcare supplier to see should you’re a candidate.”
For well being articles, please go to www.foxnews.com/well being
This research was funded by the Academy of Medicine and supported by the Dementia Research Charity Brace.

